
Tiny Batteries Could Revolutionize Green Energy
Nanotechnology could dramatically improve energy storage for electronics, cars, and buildings.
Tiny is big in the quest to build batteries that store more energy for cars, buildings, and personal electronics.
Nanosize batteries that are 80,000 times thinner than a human hair represent a promising new front. They could advance the use of electric vehicles, now limited by short driving ranges, and of renewable energy, which needs storage for times when the wind doesn't blow or the sun doesn't shine.
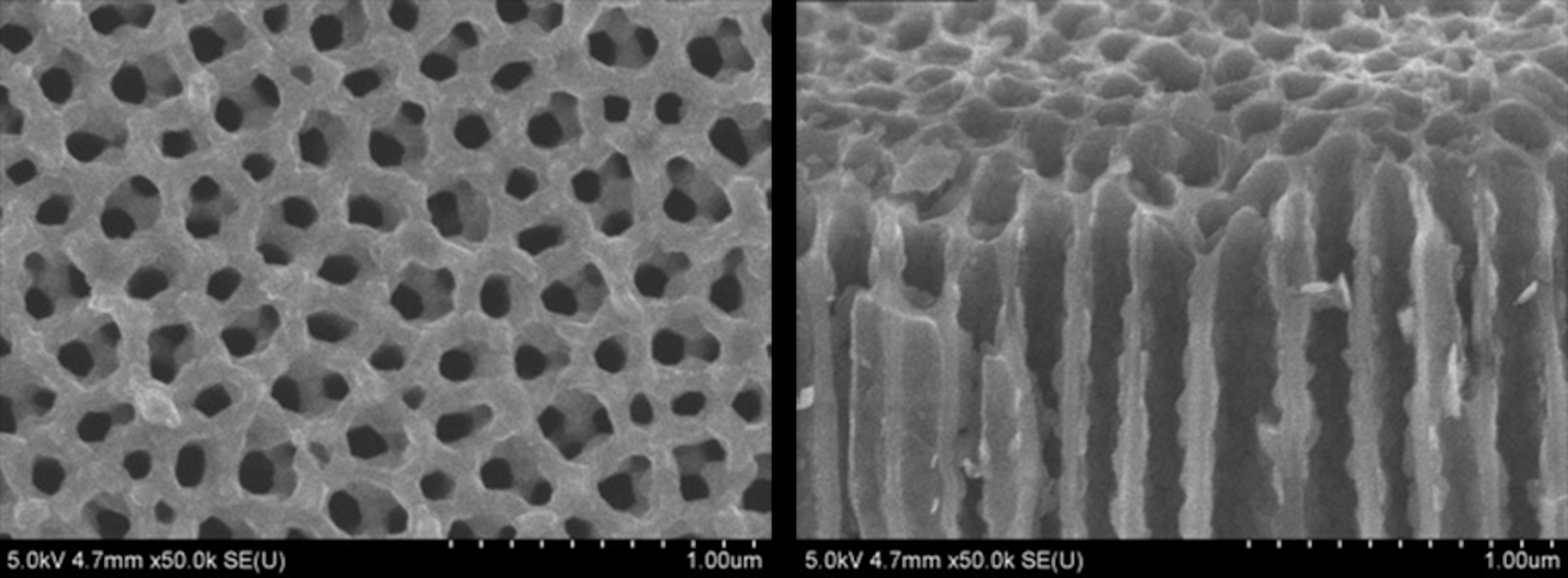
The latest breakthrough: a "nanopore" that's the ultimate in miniaturization. It's a hole in a ceramic sheet, no thicker than a grain of salt, that contains all the components a battery needs to produce electric current. One billion of these holes, connected in a honeycomb fashion, could fit on a postage stamp.
The itty-bitty battery delivers. It fully charges in 12 minutes and recharges thousands of times, according to University of Maryland researchers, who published their findings last week in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Nanotechnology.
"We were blown away by the performance," says co-author Eleanor Gillette, a doctoral candidate in chemistry. She attributes its quick charging to the short distances needed to carry the electric current. She says the nanosizing could enable manufacturers to squeeze many batteries into a tight space.
"It looks like a major advance," says George Crabtree, director of Argonne National Laboratory's Joint Center for Energy Storage Research. He says nanopores offer multiple advantages. Because they're identical, researchers-once they identify the optimal size-will be guaranteed consistent results that will make grid-scale use more promising, he says.
Crabtree says this battery, like other recent advances in nanotechnology, would not have been possible even a decade ago. Though the field has been evolving for the past 15 years, it wasn't applied to energy storage until more recently. He says it could open the door to the transformative change that's needed in the battery world.
Push for Better Batteries Expands
The stakes are immense. Electric vehicles and renewable energy, hailed as climate change solutions, need cheaper and better batteries to achieve widespread use. For utilities to rely on intermittent power sources such wind or solar for a large share of their electricity, they will need back-up energy storage. (Related: "Seven Ingredients for Better Car Batteries")
So the race is on-at universities, start-ups, and major companies like GE, IBM, and Toyota-to build a battery that goes beyond the incremental changes that have improved the performance of the lithium-ion battery, the industry standard-bearer developed in the 1970s and brought to market 20 years later.
Researchers, some with funding from the U.S. Department of Energy, are working to develop or improve several types of batteries, which produce electricity by creating chemical reactions. Most batteries have three basic parts: the electrolyte to provide electrons, the anode to discharge them, and the cathode to receive them.
By nanosizing materials and structures, scientists are trying to identify the optimal combinations at the molecular level.
Last year, for example, University of Southern California researchers developed a new lithium-ion battery that uses porous silicon nanoparticles rather than traditional graphite anodes. The team, led by Chongwu Zhou, says the battery holds three times as much energy as comparable graphite-based designs and recharges within ten minutes.
"The way to get high power is to nanosize it," says Gary Rubloff, an engineering professor who directs the University of Maryland's NanoCenter. "The world of nanoscaled batteries opens up a lot of different alternatives for how to manufacture them."
Challenges Loom in Bringing Ideas to Market
Commercializing the research won't be easy or quick. Many of the materials or assemblies in nanoscale batteries are currently too expensive for use beyond niche applications.
"Developing such batteries will be a significant challenge for the field, and questions remain," write Paul Braun and Ralph Nuzzo of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign in a commentary that accompanies the University of Maryland study and applauds its results.
Also, low oil and natural gas prices have dampened demand for renewable energy sources such as wind and solar, which require grid-scale backup batteries.
"It's hard to compete with oil and gas right now. Part of the problem is economics," says James Tour, professor of materials science and nanoengineering at Rice University in Houston, Texas. His team of researchers created a material consisting of forests of carbon nanotubes grown on sheets of graphene that could dramatically improve energy storage.
Two companies, Texas-based Xidex and Israel-based Graphite Corporation, are developing a battery based on the Rice technology that could fully charge a smartphone in a few minutes. "It might be on the market in three years," Tour says.
Stanford University professor Yi Cui says it could take three to five years to commercialize a new type of battery built by his team, which includes former U.S. Energy Secretary Steven Chu. Their battery, touted as a "pure lithium," uses lithium not only in the electrolyte but also in the anode, which is commonly graphite or silicon.
Cui's lab found a solution to a common problem: Lithium, when put in the anode, can expand more than other materials during charging and even eat up the electrolyte. To prevent this, it built "nanospheres," a honeycomb-like microscopic layer that creates a flexible nonreactive film to shield the lithium.
The team's battery, Chu said in an announcement in July, holds the potential to triple a cell phone's battery life and give electric vehicles a 300-mile driving range.
Cui has experience commercializing his research. He founded Amprius, a Silicon Valley start-up whose board members includes Chu, to sell a new type of long-lasting lithium-ion battery.
While it took two decades to bring the initial lithium-ion battery to the market, Crabtree says the current focus on energy storage-combined with the benefits of nanoscience-may expedite that process to between five and 10 years.
"It's really a moment of opportunity right now," he says. "There's an opportunity to accelerate the pace of innovation."
On Twitter: Follow Wendy Koch and get more environment and energy coverage at NatGeoGreen.
The story is part of a special series that explores energy issues. For more, visit The Great Energy Challenge.