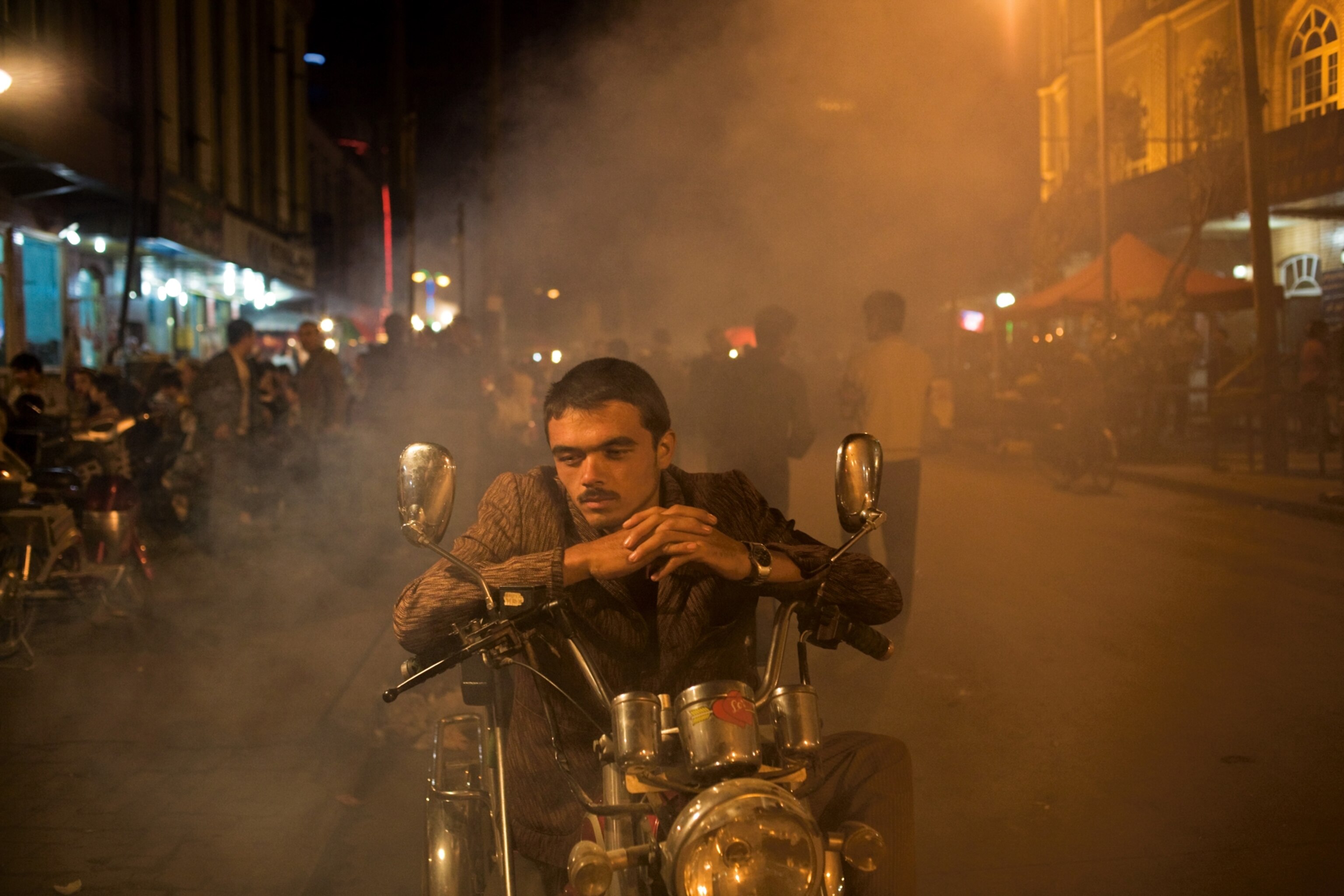The Other Tibet
The Uygurs, Muslim people of China’s resource-rich far west, are becoming strangers in their own land as Han Chinese pour in. Like the Tibetans, who face similar pressures, some Uygurs see a chance for a better life, but others protest the disintegration of their culture, even at the risk of death.
The first several seconds of the incident in Urumqi seemed almost lighthearted, considering the previous week. And they revealed nothing about what would follow. A cool front had swept over the city on this particular day in July, drawing people from their homes. Some shops stayed closed because their windows had been shattered, but food vendors pushed their carts out onto the street. A week earlier an ethnic clash had broken out here, killing almost 200 people in one of China’s most deadly protests since the Tiananmen Square massacre two decades ago. So the Chinese government had sent tens of thousands of security forces into the city, the capital of the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, to restore order between the Han and the Uygurs. The Han dominate Chinese society, but the Uygurs (pronounced WEE-gurs), a Turkic-speaking Central Asian people, claim this western borderland as their ancestral home.
Han security forces stood in ranks along every street in the city's Uygur quarter. They bristled with riot gear and automatic weapons. The only sound came from loudspeakers mounted on trucks that trawled the market streets, broadcasting the good news of ethnic harmony. If Urumqi had an edge of unrest on this Monday, it was sheathed in silence.
Most Uygurs are Muslims, and about noon I stood on the street in front of a central mosque wondering how many people might be inside. As if in answer, a mass of humanity came pouring out, hundreds of people tumbling and plunging into the street.
Bystanders watched, puzzled, but the emerging crowd offered only odd and inscrutable clues: Many hadn't had time to pull on their shoes and ran in just their socks. They cried out with alarm or possibly in celebration, and their faces glowed with either fear or joy. If they were fleeing from danger, there was no sign of it, and the group split and flew north and south. In the flicker of a moment they had disappeared.
Now three men stepped from the mosque, holding what looked like wooden sticks. One wore a blue shirt, one a black shirt, and one a white shirt. They shouted and smiled, which gave their faces a buoyant quality. Their tiny rally seemed brash: Did they not see the Chinese police on every corner or hear the amplified news about manifest happiness?
They turned southward. All three walked with peculiar long strides and waved their sticks overhead, like three baton-twirling drum majors whose marching band had run ahead of them. They passed rows of market stalls where people shouted to them to stop whatever they were doing. Shop owners slammed shut their stall doors. After two blocks the men stopped and turned back north; just before they reached me, they crossed the street. They still held up what were, more likely, rusted swords.
Once across the street, they burst into a run, heading toward a group of armed Chinese. The man in blue sprinted ahead; he seemed to catch the government forces off guard, because they turned and ran. The details of the next moment—the angle of the running man, his shirt billowing behind him, the strange coolness of the air—were etched by a sound: a gunshot. But the three Uygurs did not stop in the face of destruction. They tilted toward it.
The Tibetan struggle for independence from China has long captivated the West. Fewer people are familiar with an arguably more critical struggle in a neighboring hinterland: that of the Uygurs. Their anonymity is ironic because the West has played an unwitting role in their current crisis—and because the Uygurs, whose culture is fading toward obscurity, once occupied the center of the known world.
Xinjiang sits in the middle of Asia, encircled by some of Earth's highest mountains, as though a drawstring had cinched the top of the world like a coin purse. Passes through those snowy mountains funneled ancient traders and travelers along paths that became the renowned Silk Road. "They say it is the highest place in the world," Marco Polo wrote of climbing the Pamir mountains from the Afghanistan side. When he emerged from the pass, he found the Uygur homeland and marveled: "From this country, many merchants go forth about the world."
The territory became the fulcrum on which Asia and Europe balanced. Turkic raiders and later Genghis Khan, Buddhists and then Muslims, traders and tribesmen, missionaries and monks—all passed through this hemispheric crossroads, and each group left something of itself. I saw a Uygur woman wearing a Muslim head cover and holding her baby, whose head she had shaved into phantasmagoric designs, a pre-Islamic shamanistic practice to frighten away baby-stealing evil spirits. Xinjiang's history is also written in the faces of its people: dark faces with oval eyes. Also fair faces with narrow, jet eyes. And sometimes blue eyes with blond hair.
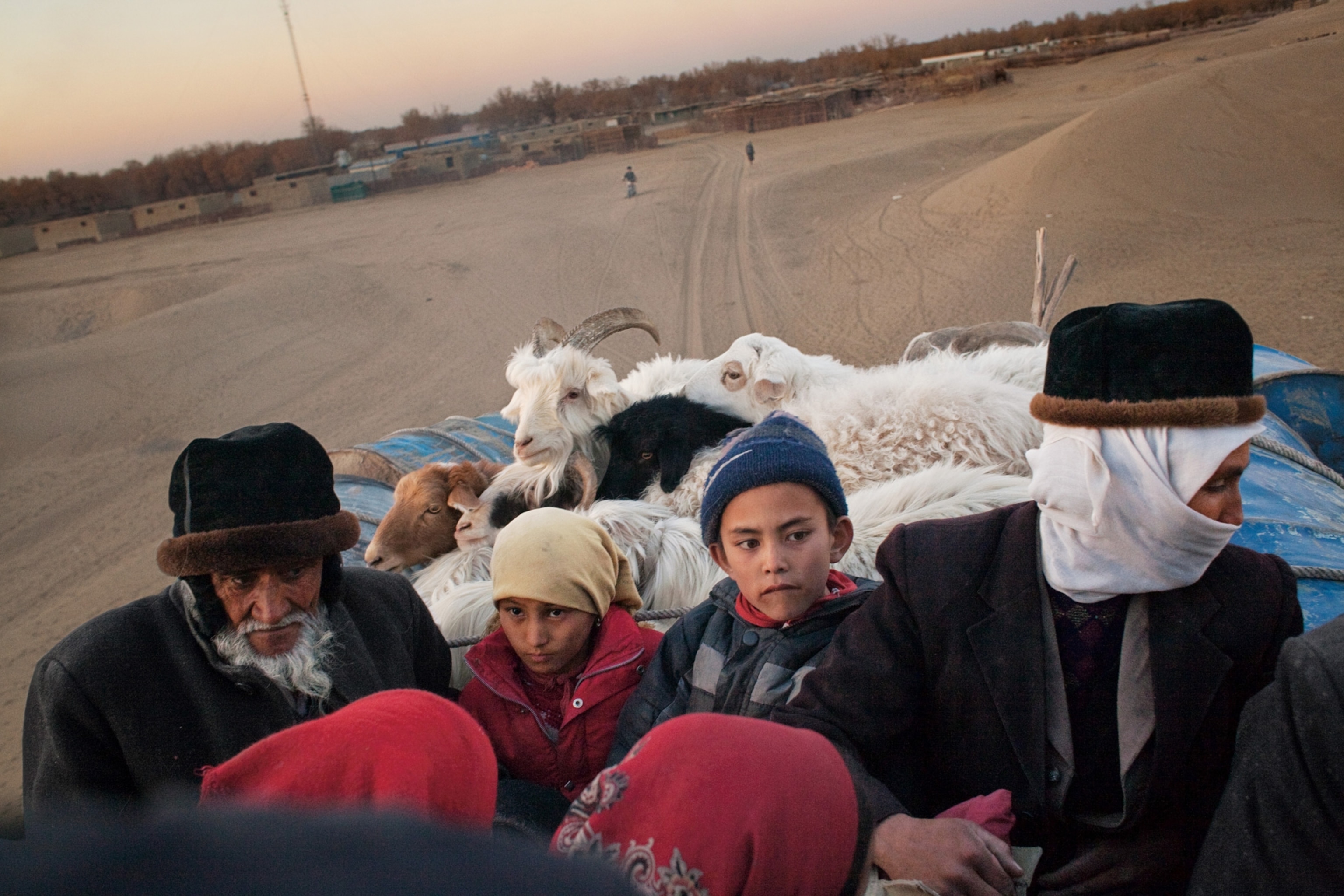
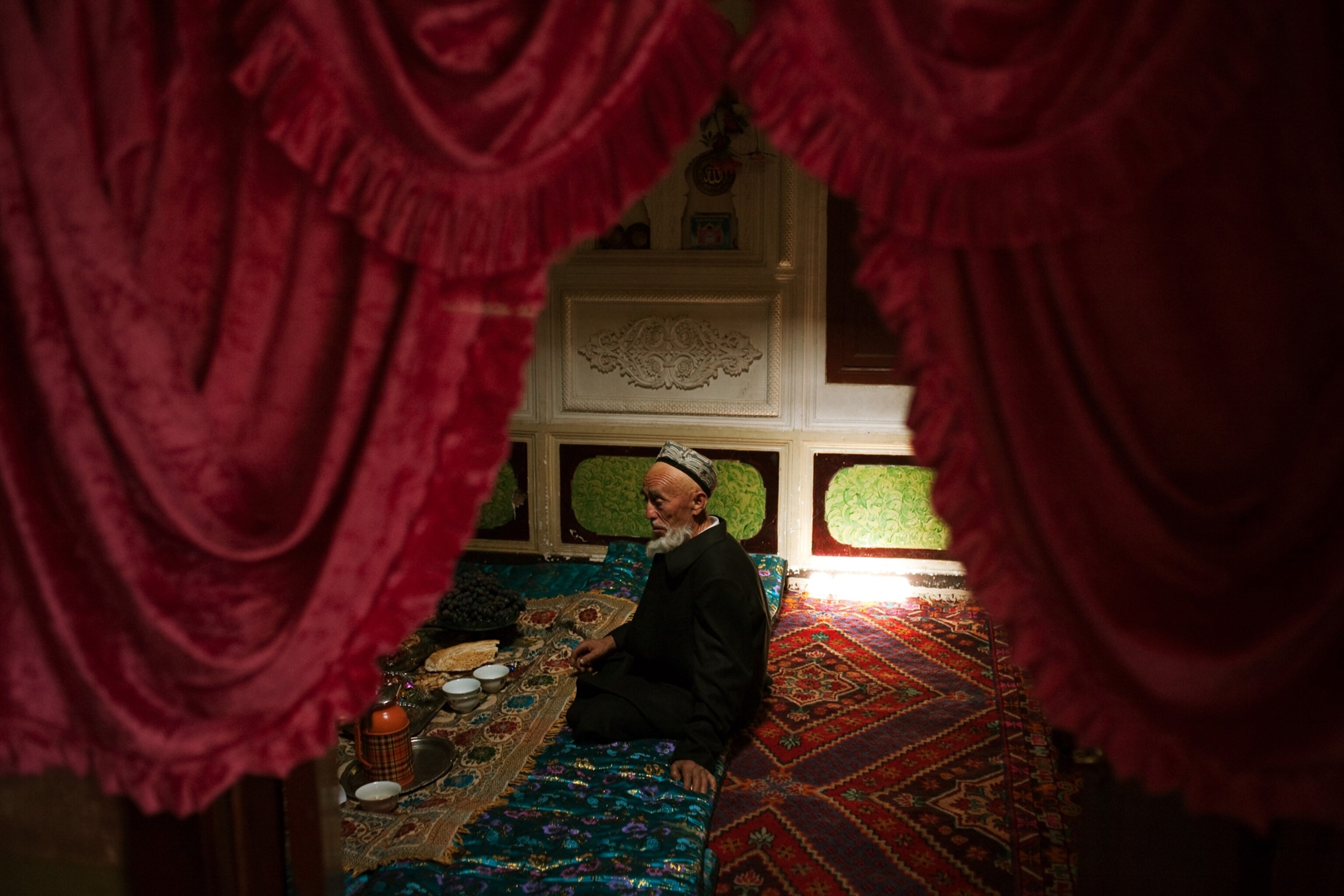
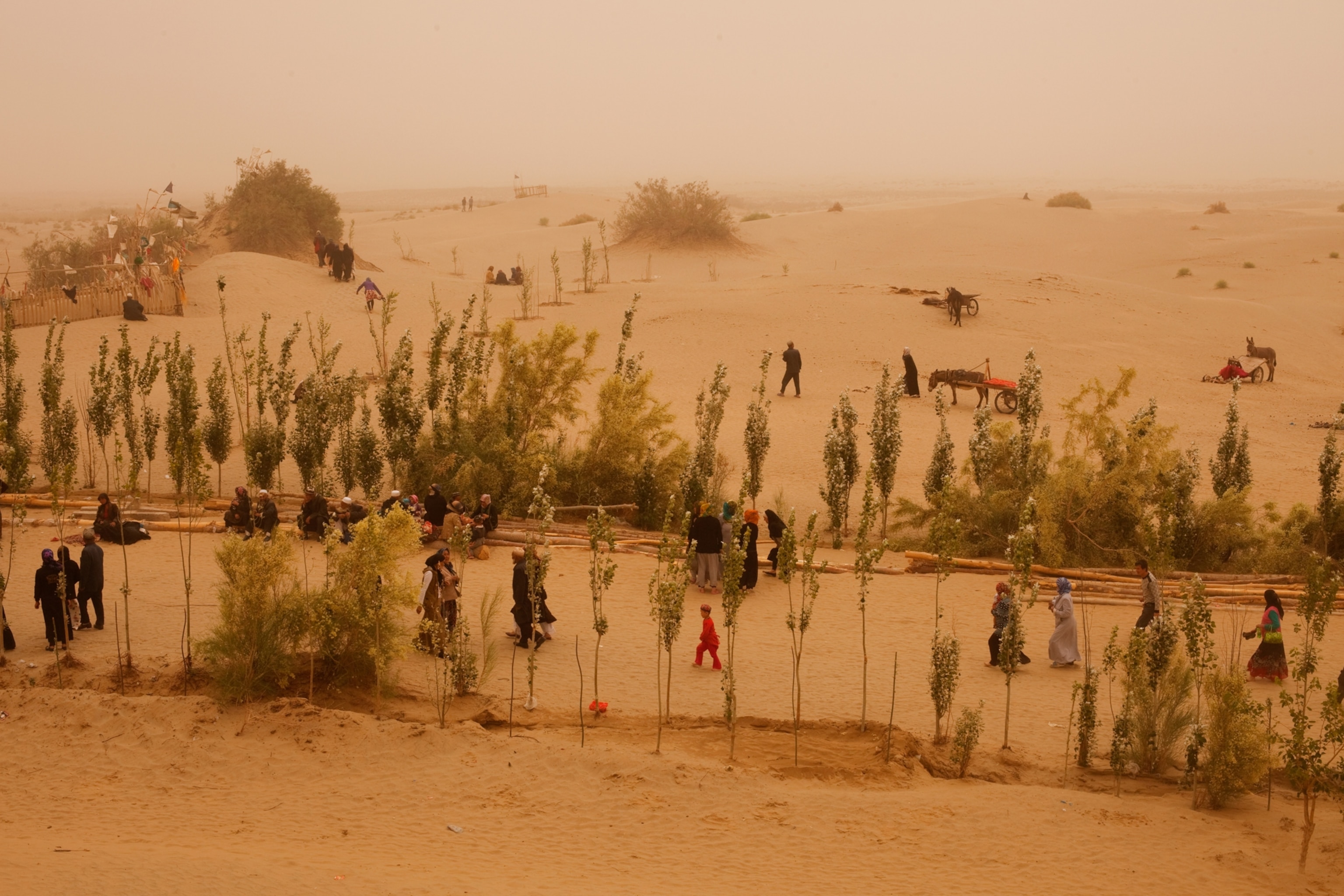
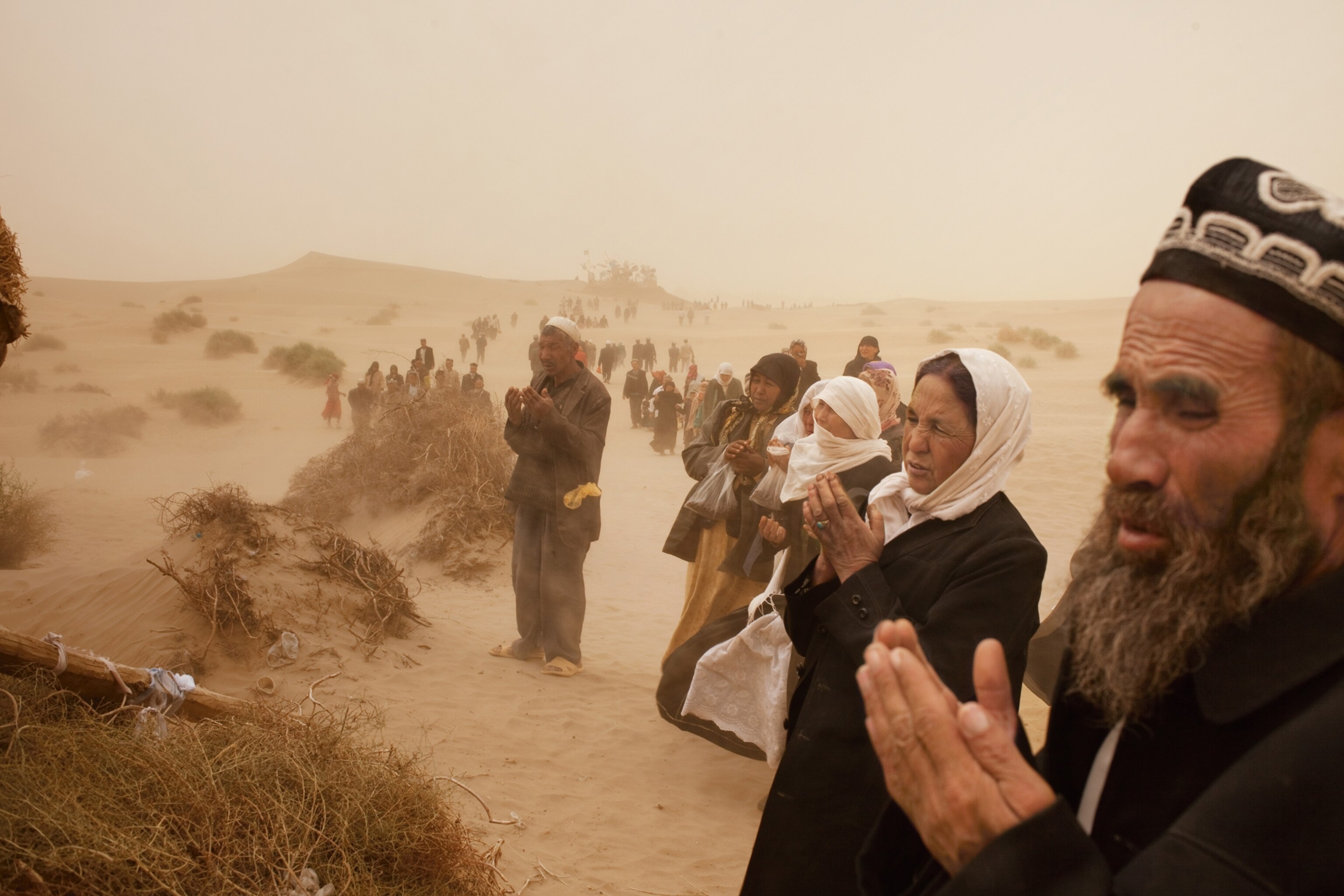
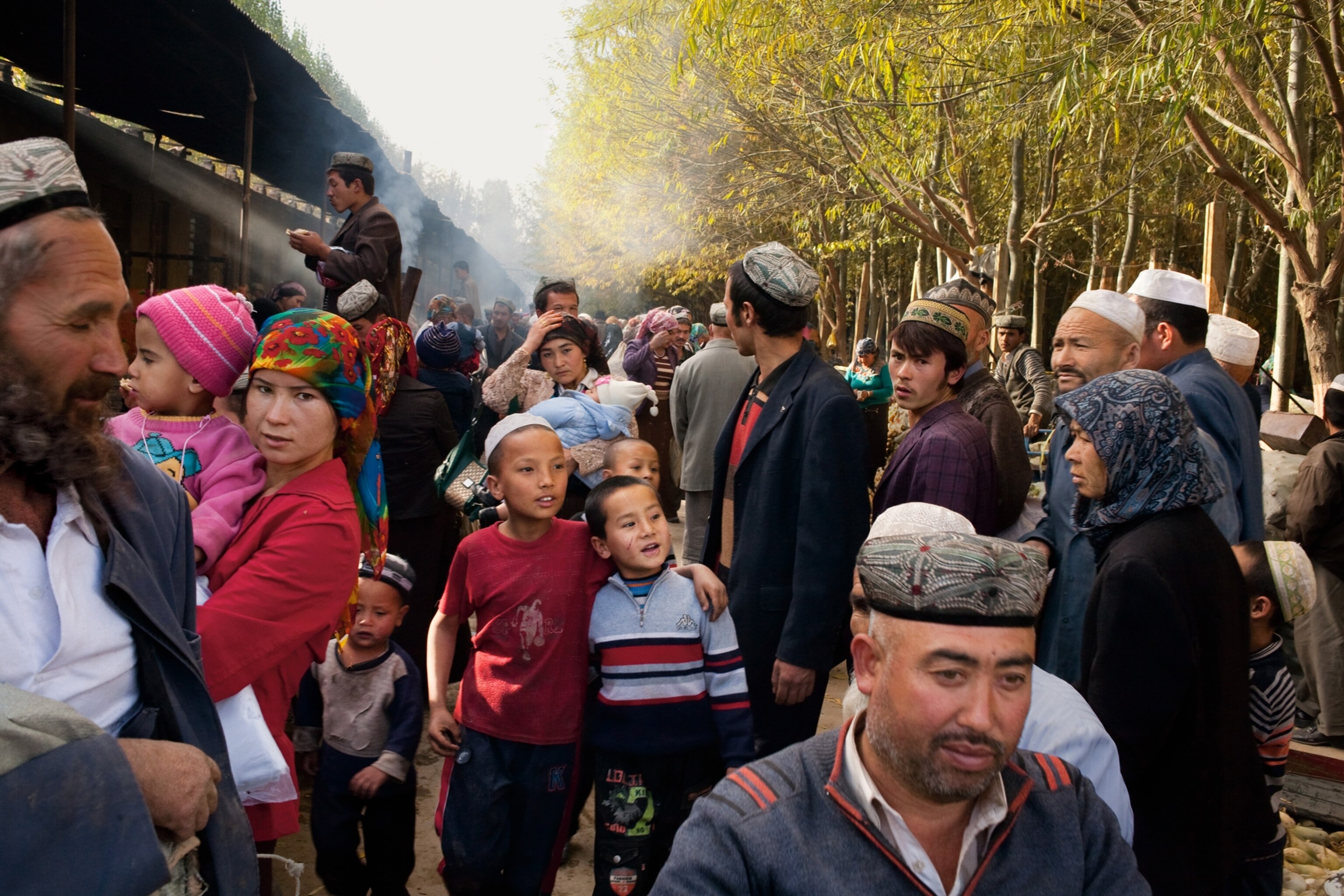
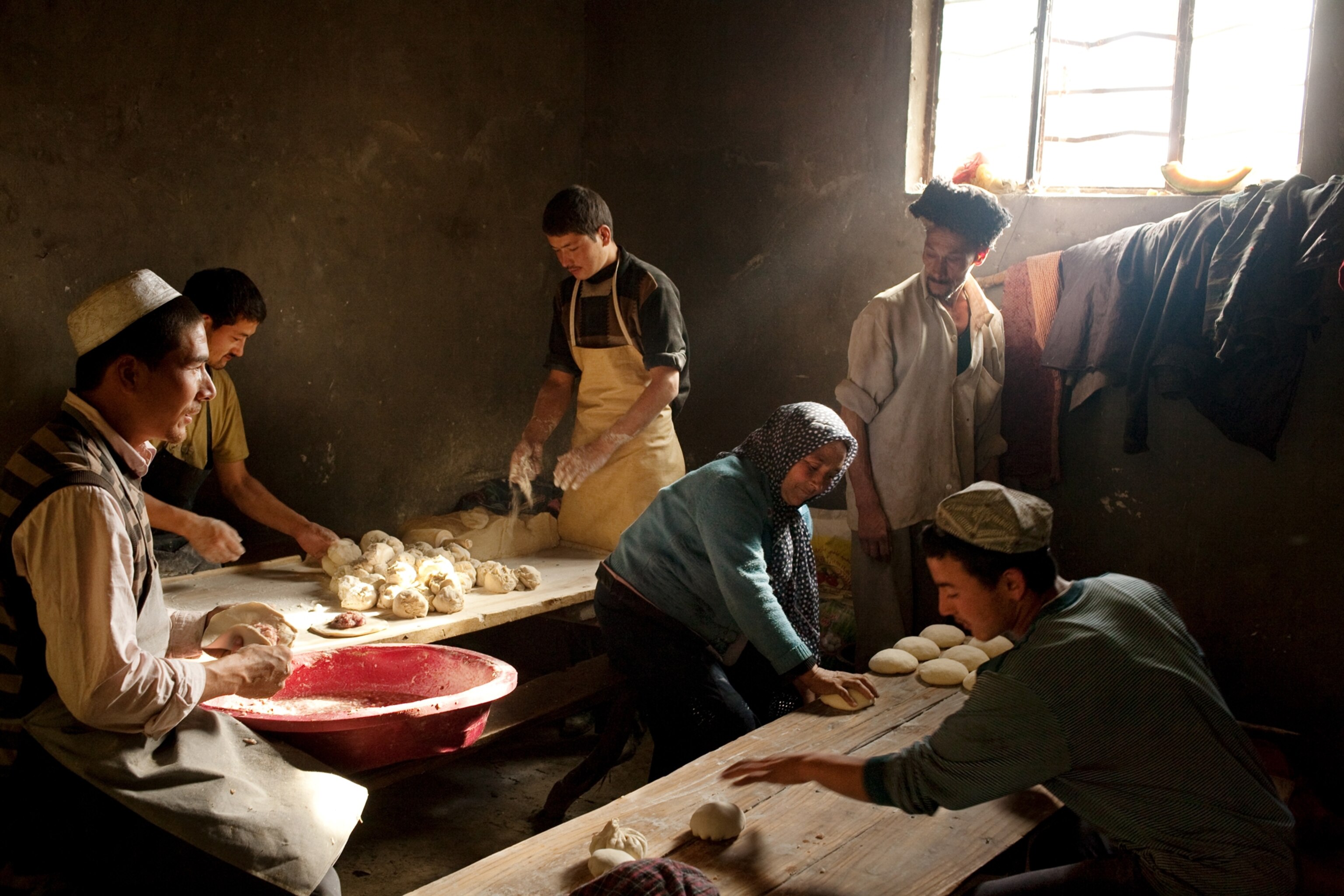
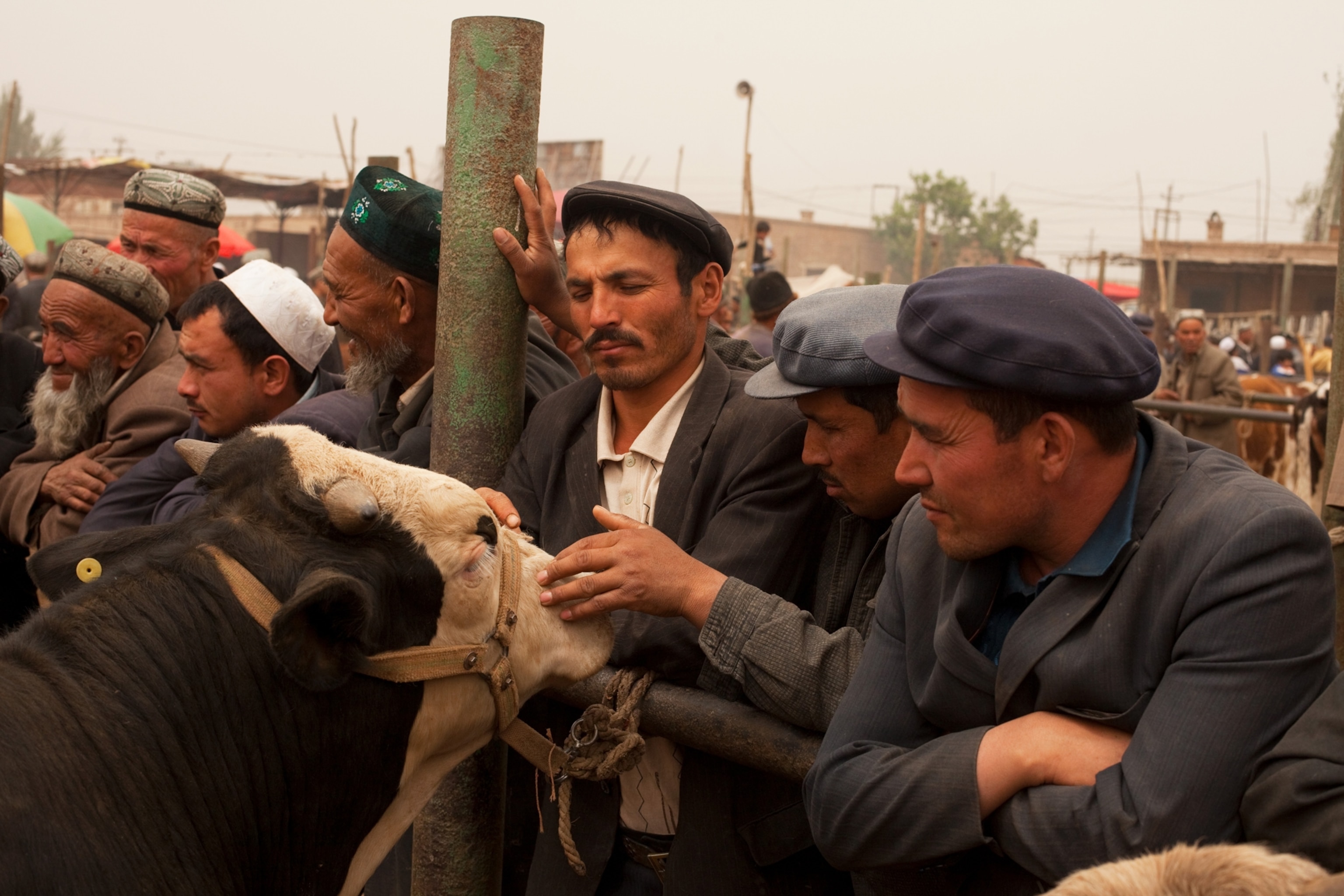
Geography itself protects the mosaic of Uygur culture in Hotan, in far southwestern Xinjiang. A range of snowcapped mountains rises at the town's back, and before it lies the Taklimakan, a desert larger than Poland, which people sometimes call the Sea of Death. Hotan's inhabitants are mostly farmers, and many of them come together each Sunday outside the town for a bazaar where children eat sweetened ice shaved from chunks that float down the Karakax (Black Jade) River, women browse tents full of silk, and men gather to have their beards trimmed while they tell jokes.
It's an old scene, although there is an occasional sign of technology: Knifemakers sit in long rows on ancient bicycles they've reconfigured to spin grindstones, looking like an invading horde of spark-spitting cyclists. A young Uygur man named Otkur (the names of Uygurs in Xinjiang have been changed for their protection) shared his bowl of sheep's lung with me, and afterward we approached an astonishing device: a two-story-high swing set with a seat big enough for two people to stand on. Otkur smiled. "For playing," he said. Two women climbed onto the ends of the seat and swung so high they disappeared into tree branches.
In town I met Dawud, a music master who teaches a small group of students. In his school a large mural showed a mashrap, a traditional all-male gathering—now closely regulated by the Chinese—where Uygurs convene to play music, recite poetry, and socialize. Dawud fashioned a fingerpick from a piece of wire and some twine, flicked his fingers across the five strings of a tambur, and launched into a series of complex songs with roots that reach back at least five centuries.
Those patchwork elements of Uygur life underscore something crucial about the Uygurs as a whole: Centuries of living at a great Eurasian way station have made them a complicated people who defy careless classification. But in time the world forgot this, with disastrous results.
As the Silk Road began to fray and trade took to the seas, both East and West lost interest in the Uygurs and their mountain fastness. For generations China saw little promise in this remote land—Xinjiang means "new frontier"—because the Chinese prized agriculture, and the wild west offered only dust and stones. People there ate mutton, not pork. In 1932 a British officer traveling in Xinjiang wrote with dark foresight, "Perhaps an awakening China, wondering where to settle its surplus millions of people, may have the good sense to call in the science of the West and to develop [Xinjiang]." But through the early 20th century, the Chinese government did not extend its influence to the distant region, and the Uygurs twice declared their own independent country. The second attempt at self-determination, in 1944, lasted five years, until the rise of Mao and the Chinese Communist Party, which sent in military forces and later established a nuclear testing ground, Lop Nur, in Xinjiang to eliminate any confusion.
Realizing that, if nothing else, its big, empty territory provided a buffer against foreign influence, Mao's China instituted a program called the Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps—combining farm, military garrison, and prison—in which settlers from other Chinese provinces would work the soil and watch the borders. The first arrivals, in 1954, included more than 100,000 demobilized soldiers. Some were coerced, but the flow gathered momentum as the government extended a railroad west to Urumqi in 1962 and used promises of food and clothing to entice residents from overcrowded cities like Shanghai.
Meanwhile the Chinese were discovering that Xinjiang offered far more than just a border cushion: It held something vital to their very survival as a nation. Xinjiang contains about 40 percent of China's coal reserves and more than a fifth of its natural gas. Most important, it has nearly a fifth of the nation's proven oil reserves, although Beijing claims it holds as much as a third. Never mind the massive deposits of gold, salt, and other minerals. Xinjiang isn't empty. It's strategic. And with that realization, other things came sharply into focus for China's leadership: Xinjiang is the largest, most far-flung region. It borders more countries than any other. And it's home to an ethnic group that has tried twice in living memory to make a break for freedom.
In 1947, during the second incarnation of Uygur independence, about 220,000 Han Chinese made up 5 percent of Xinjiang's population. Uygurs numbered about three million, or 75 percent, the remainder being a mix of Central Asian ethnicities. By 2007 the Uygur population had increased to 9.6 million. But the Han population had swelled to 8.2 million.
Some Uygurs found opportunity in the influx. In the 1980s in burgeoning Urumqi, a laundress named Rebiya Kadeer grew her business into a department store, then built that into an international trading empire. She became one of the wealthiest people in China and an inspiration for her compatriots—a Uygur woman who appeared in Asia's Wall Street Journal and met with such businessmen as Bill Gates and Warren Buffett. In many ways she seemed emblematic of Xinjiang: In the last two decades of the 20th century the region's GDP increased tenfold.
But many more Uygurs languished. The big business in Xinjiang is oil, but all that oil is controlled from Beijing by state-owned energy companies. Many of the good jobs in Xinjiang are government jobs, and employees can advance more readily if they join the Communist Party, which requires renouncing their religion. And most Uygurs won't do that. The result is an ironic and combustible symmetry: As Han settlers pour in, Uygurs, unable to find work in their fantastically wealthy and spacious homeland, migrate east to work in privately owned factories in crowded coastal cities.
In the past few decades local resistance has flared up around Xinjiang, fluctuating in scale and violence. During the 1980s Uygur students protested treatment by police in a handful of incidents; in 1990 a disturbance south of Kashgar against birth limits ended in perhaps four dozen deaths. In 1997 hundreds of people in a city called Gulja marched to protest repression of Islamic practices and were arrested; the number of casualties is unknown. Other examples abound, including bus bombings and assassinations.
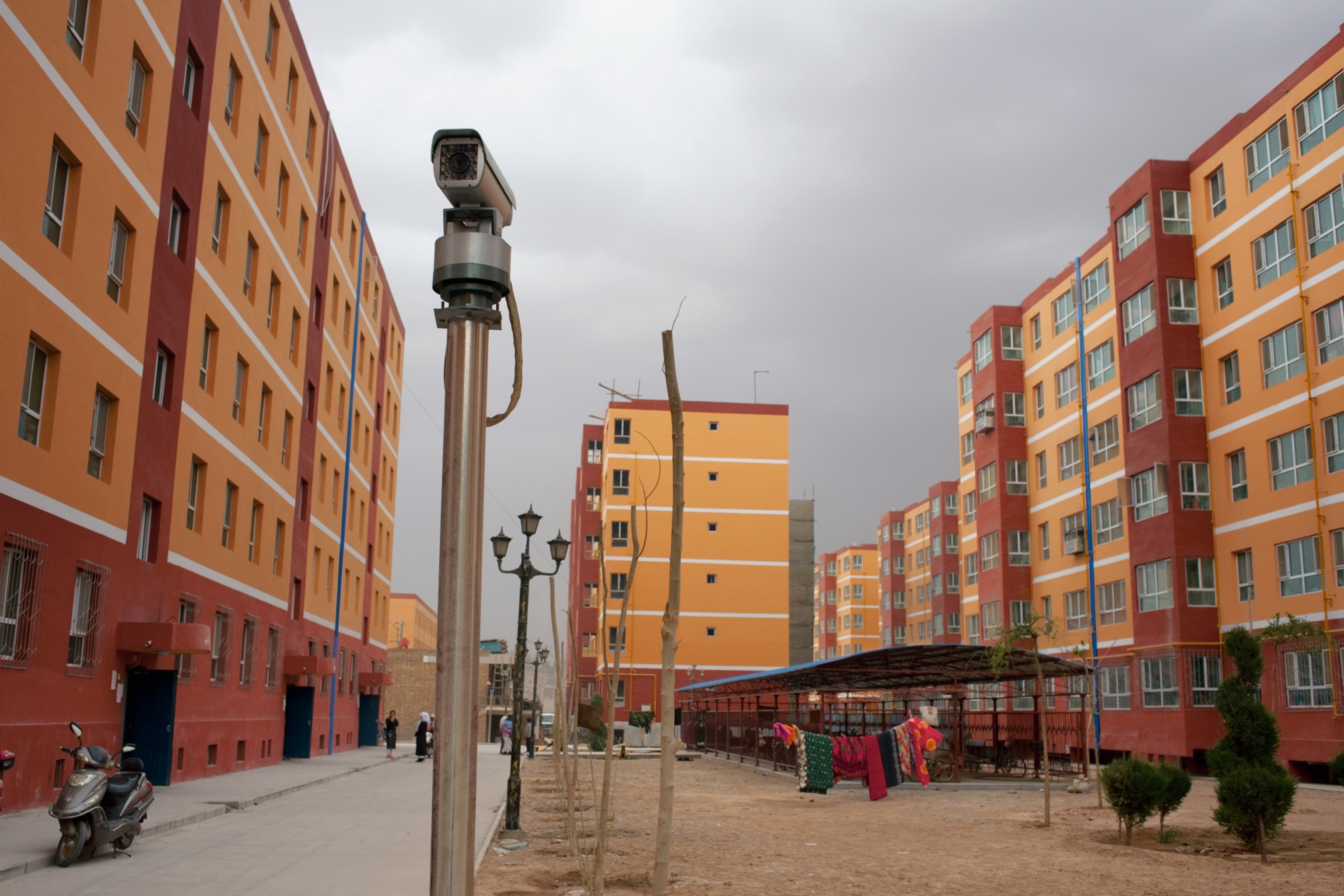
The Chinese government realized that it had a problem in Xinjiang, much as it had a problem in neighboring Tibet. Along with regulating mashraps—those traditional gatherings—the state monitored services at mosques, afraid they might provide a platform for dissidents. In general, officials downplayed the unrest as the work of isolated "ruffians" in a Uygur population that was otherwise blissful. In early September 2001, Xinjiang Communist Party Secretary Wang Lequan announced in Urumqi that "society is stable, and people are living and working in peace and contentment."
A few days later Beijing received a potent and unexpected propaganda tool: September 11.
As America and much of the West launched the "war on terror," China recognized the momentum of global public opinion and chose a new tack. The shift happened so fast it came with an almost audible crack. On October 11 a spokesman for the Chinese Foreign Ministry described China as "a victim of international terrorism." Then the government issued a report on unrest in Xinjiang blaming none other than Osama bin Laden. "It's an effective strategy," says James Millward, a professor at Georgetown University and an expert on Xinjiang, "because in America we see Muslims somewhere who are unhappy and maybe even violent, and we assume it's because of religious reasons."
And just like that, the Uygurs—with the complexity of their culture, the richness of their past, the fullness of their grievance against the Chinese state—fell into a tidy classification. China asked the United States to include a group of militant separatist Uygurs on its list of terrorist organizations but was rebuffed—at least at first.
In December 2001, 22 Uygurs were captured in Pakistan and Afghanistan, where they may have received weapons training with the intent of battling the Chinese military back in Xinjiang. The men were rounded up by bounty hunters, handed over to U.S. forces, and sent to Guantánamo Bay. (Years later a U.S. court would order their release.) In August 2002 Deputy Secretary of State Richard Armitage traveled to Beijing to discuss, among other issues, America's upcoming mission in Iraq. While there, he announced a reversal in the U.S. stance: A militant Uygur group called the Eastern Turkistan Islamic Movement would now be listed as a terrorist organization.
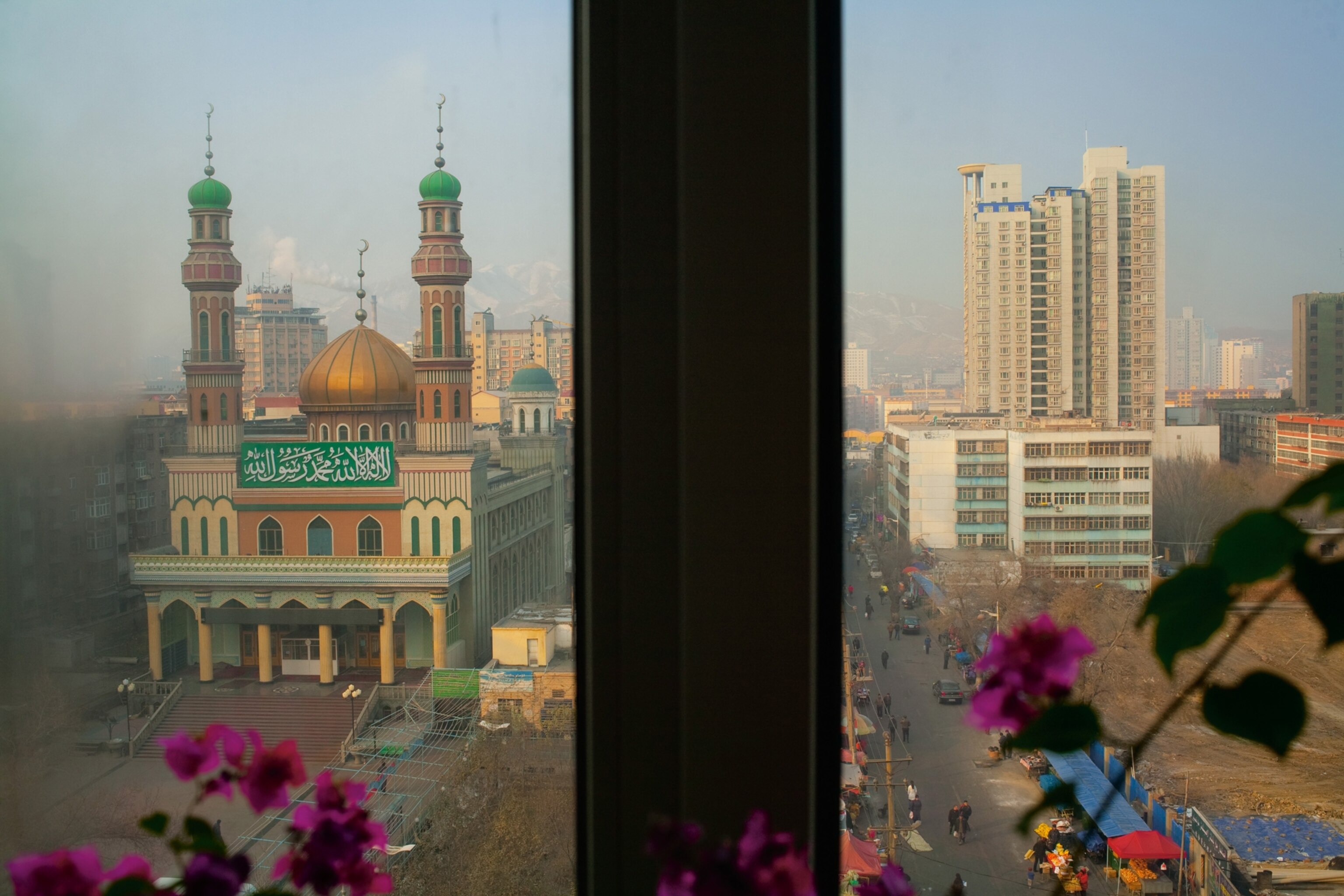
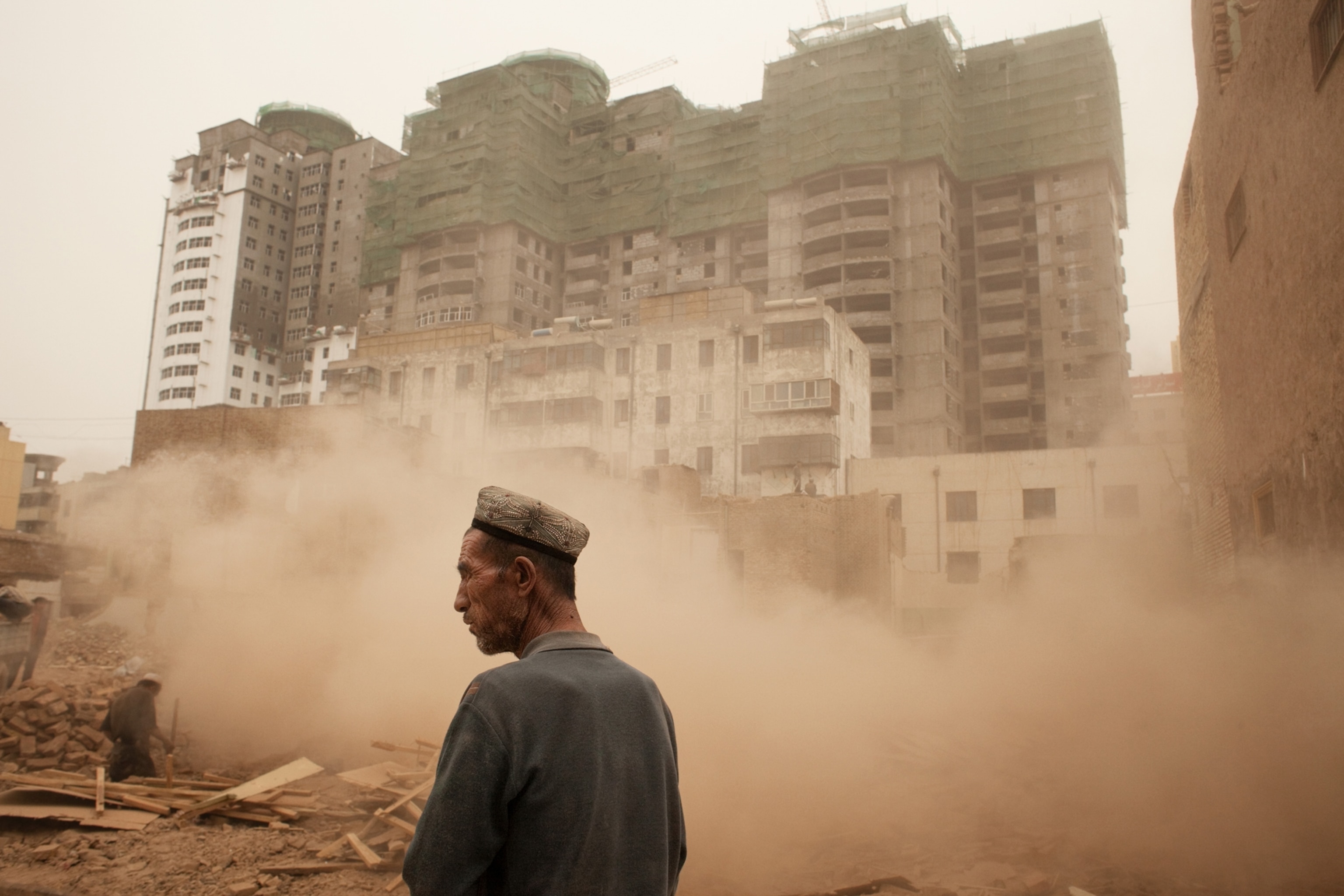
The heart of Uygur tradition is the ancient capital of Kashgar. Today its Old City looks much as it must have when Marco Polo spied it after descending through the mountain pass—a warren of passageways and ancient mud-brick homes that resemble a jumble of oversize children's blocks. Early this year the Chinese government undertook a bold step: They began systematically bulldozing the Old City block by block and moving the inhabitants into a new compound on the edge of town.
Uygurs don't discuss the subject in public for fear of imprisonment, but one man who lives in the Old City, Ahun, agreed to talk with me in his home. A rendezvous would not be easy, because for days the Chinese security services had been following me. I was to wait in the main square during the busy midday until I saw him pass under Mao's statue, then follow at a distance without acknowledgment.
As we walked through city streets, he stopped casually to take a drink of water at a cart and later to tie his shoe. Finally we entered the Old City. The Chinese government's ostensible reason for demolishing the neighborhood is that it's too old to withstand an earthquake. But there may be another motive. As Ahun and I wove our way deeper into the warren, I watched his shoulders relax and his gait loosen. He was hard to trace in here. The Old City is a refuge.
The homes are adjacent and interconnected, and each is two stories high and arranged around a central courtyard. I followed Ahun up a flight of stairs, and when he flung open the door, it struck me that these homes are like oysters: On the outside they're drab and crude, but on the inside whitewashed plaster walls gleam, and many-colored rugs complement painted ceilings. "I pray. When I worship, I ask Allah, 'Rescue me my house,' " Ahun said. From his house he has a clear view of a government wrecking crew at work on a nearby home. According to the demolition schedule, they'll arrive at Ahun's home in three years.
He was born in the house, he said. So was his father. So was his grandfather, after his great-grandfather built it on family land. "I have two sons," he said. That's five generations who have lived in the same house.
If Hotan represents Xinjiang's past—with a Uygur majority that gathers to sharpen knives, trim beards, sing songs—then Kashgar is its present. Uygurs still make up most of the city's population, but their culture here is embattled. The government is working fast to tear it down.
Given enough time, Ahun said, China's economic development will bring political change, and hope for his people. "China will be obliged to receive a democratic system," he said. But right now, for a man who prays each day for the survival of his family home, no act is too desperate. "You do not understand our rage," he said. "In the Middle East there are human bombs, who connect their bodies with bombs. But with our rage, we don't need bombs connected. We ourselves explode."
In June of this year, a disgruntled worker at a toy factory in Shaoguan, near Hong Kong, reportedly claimed that Uygurs had raped two women. A melee followed. The violence lasted several hours and left scores injured. Angry Han workers in the factory's dormitory beat to death two Uygur co-workers.
This spark lit a fire 2,000 miles away, in Xinjiang. On July 5 thousands of Uygurs—the numbers reported varied widely—took to Urumqi's streets to protest the treatment of the Uygur workers. The authorities were caught off guard.
I spoke to a young woman named Arzigul, who had attended the protest. She said it started off peacefully as young people circulated around the capital's public square. "They were screaming the name 'Uygur! Uygur! Uygur!' " she said. When security forces arrived, something happened—exactly what is unclear. Each side says the other struck first, but at some point the authorities tried to quell the crowd, which apparently devolved into a mob attacking Han on the street. Two days later a group of Han—apparently numbering in the thousands—took to the street with meat cleavers and clubs and knives. They in turn attacked Uygurs.
Chinese officials say they're protecting their citizens from terrorists. In July, Vice Foreign Minister He Yafei called the riots "a grave and violent criminal incident plotted and organized by the outside forces of terrorism, separatism, no comma after separatism in original source and extremism." James Millward, the Xinjiang expert, says many Han—even officials—sincerely believe Xinjiang faces a threat from terrorists and interlopers. "It's what they are constantly told." Eventually military forces and police clamped down on Urumqi, and there seemed no possibility of further unrest. That's when the three men emerged from the mosque in the Uygur quarter, scattering people in every direction.
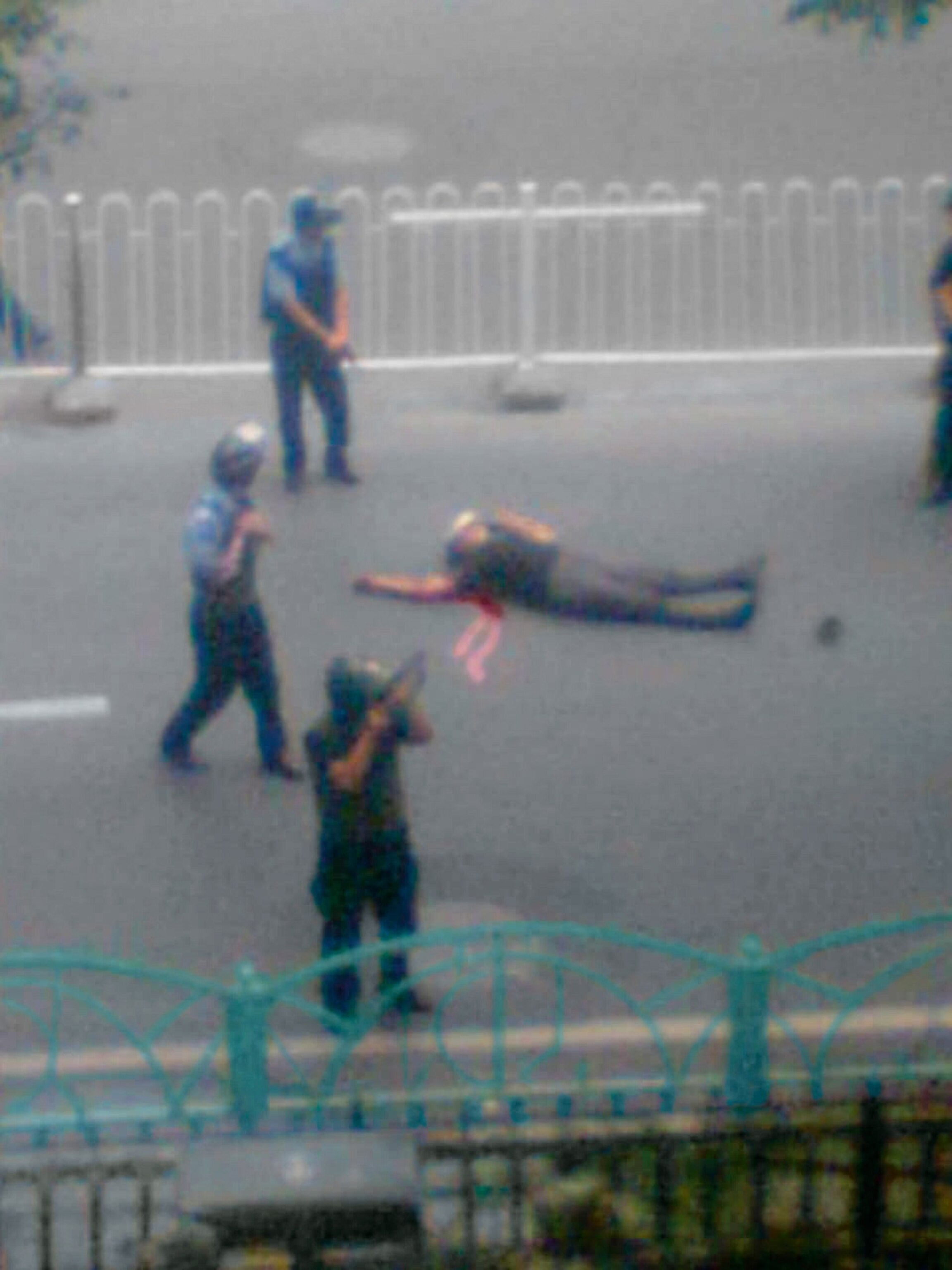
I watched them stride up the street and back, then run at the Chinese forces. First came the single shot, which missed. The Uygurs continued their charge, and I realized that the running men with their rusted swords did not expect to prevail. They expected to die.
A moment later another officer released a burst of automatic fire. The lead Uygur—the man in the flowing blue shirt—fell with the sudden slackness of a thrown rag doll. His body hit the pavement, but the momentum of his sprint sent him tumbling, and his feet flew up and over his head.
For a few seconds the incident played out in tableau on the opposite sidewalk. The remaining two Uygurs ran into the street, and the scene became three-dimensional, with bullets flying in my direction. I ran into a nearby building and found myself in the lobby of an enormous department store. People pressed themselves into corners and behind clothing displays; women wailed, and two men improvised a door lock by shoving a metal bar through the door's handles. Beyond the building's glass doors, all three of the Uygur men now lay in the street, one injured and two dead. Soldiers, police, and plainclothes security officers were firing upward, into the windows of surrounding buildings.
The department store held special significance for the Uygurs. It belonged to their heroine Rebiya Kadeer, the laundress turned mogul who had become beloved after she began to speak out against China's treatment of the Uygurs. In 1999, as an American delegation arrived in China to meet Kadeer, security officers arrested her. She spent the next six years in prison, then joined her exiled husband in the U.S. Her imprisonment only raised her status among her people, who regard her as the "mother of all Uygurs."
She's a grandmother, just over five feet tall, and she terrifies the Chinese authorities. Mentioning her name in Xinjiang brings swift and severe punishment. When I went with Ahun to his home in Kashgar's Old City, he spoke freely of rebellion against China's government, but when I mentioned Rebiya Kadeer, he froze. "If China finds this," he said, pointing to my voice recorder and then reaching for my throat in mock vengeance, "on Judgment Day I will catch your neck."
After the July riots, trucks with loudspeakers circled the public squares of Urumqi, proclaiming that the unrest had been organized by Kadeer from her office in Washington, D.C. Chinese officials accused her in news reports around the globe and were said to be planning to tear down her trade centers. "The Chinese authorities are fearful of me because of what they have been doing to the Uygur people," she told me recently. In her office an enormous East Turkistan flag—symbol of a free Uygur nation—hangs on one wall, and photos of her 11 children, two of whom are in prison, hang on another.
The Western world knows of the struggle for freedom by Tibetans largely because the Dalai Lama presents a warm and charismatic embodiment of his people. The Uygurs have remained obscure, in part, because they have no such figure. But the Chinese government's recent efforts to demonize Rebiya Kadeer have lifted her into a representative role. "I keep advocating for my people, for the self-determination of Uygurs," she told me. Whether that means autonomy within China or a push for full independence depends on the government's reaction, she said. "At the moment I'm trying to invite the Chinese authorities to come to the dialogue peacefully."
Even as Kadeer spoke, another round of strife loomed in Xinjiang—rumors, allegations, protests—and she acknowledges that a peaceful resolution may be impossible. After seeing the region's past and present through Hotan and Kashgar, we may be glimpsing its future in Urumqi: a sprawling city that serves Han migrants drawn by Xinjiang's natural resources, where a Uygur minority stays confined to its quarter.
And on an otherwise silent Monday afternoon, men detonate on the street from the sheer force of their rage.