This Week’s Night Sky: A Lion Makes a Meteoric Roar
Dozens of shooting stars from the annual Leonid meteor shower will streak across the sky mid-week.
Zodiacal Lights. Throughout the week, just before local dawn and under very dark skies, the ghostly glow of the zodiacal lights will be visible across mid-northern latitudes around the globe.
Easily mistaken for lights from distant cities or even the faint radiance of the Milky Way, the pyramid-shaped glow above the eastern horizon is caused by sunlight reflecting off dust particles spread out between the planets in our solar system.
Morning Planet Show Continues. All week long, the three brightest planets in the early eastern morning skies—Mars, Jupiter, and Venus—continue the dramatic display that they began last week. However, the show will soon come to a close as the three worlds are slowly pulling apart, with Venus sinking closer and closer to the horizon and the sun, leaving Jupiter and faint ruddy Mars behind.
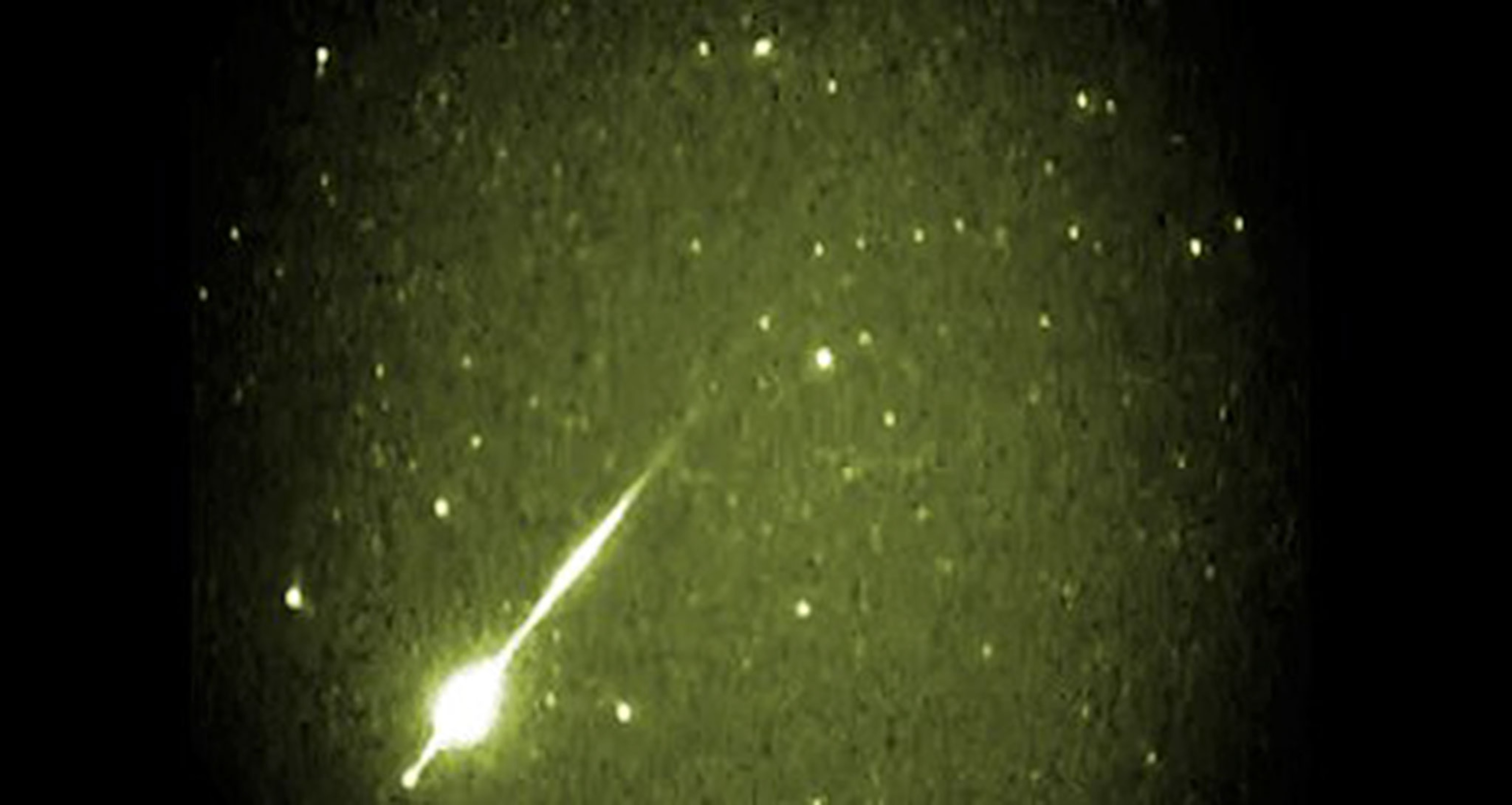
Leonid Meteor Shower. Late night on Tuesday, November 17, look for shooting stars to streak across the sky every few minutes. This is the annual Leonid meteor shower, and under dark skies, as many as 10 to 20 meteors per hour may be seen radiating from the constellation Leo, the lion.
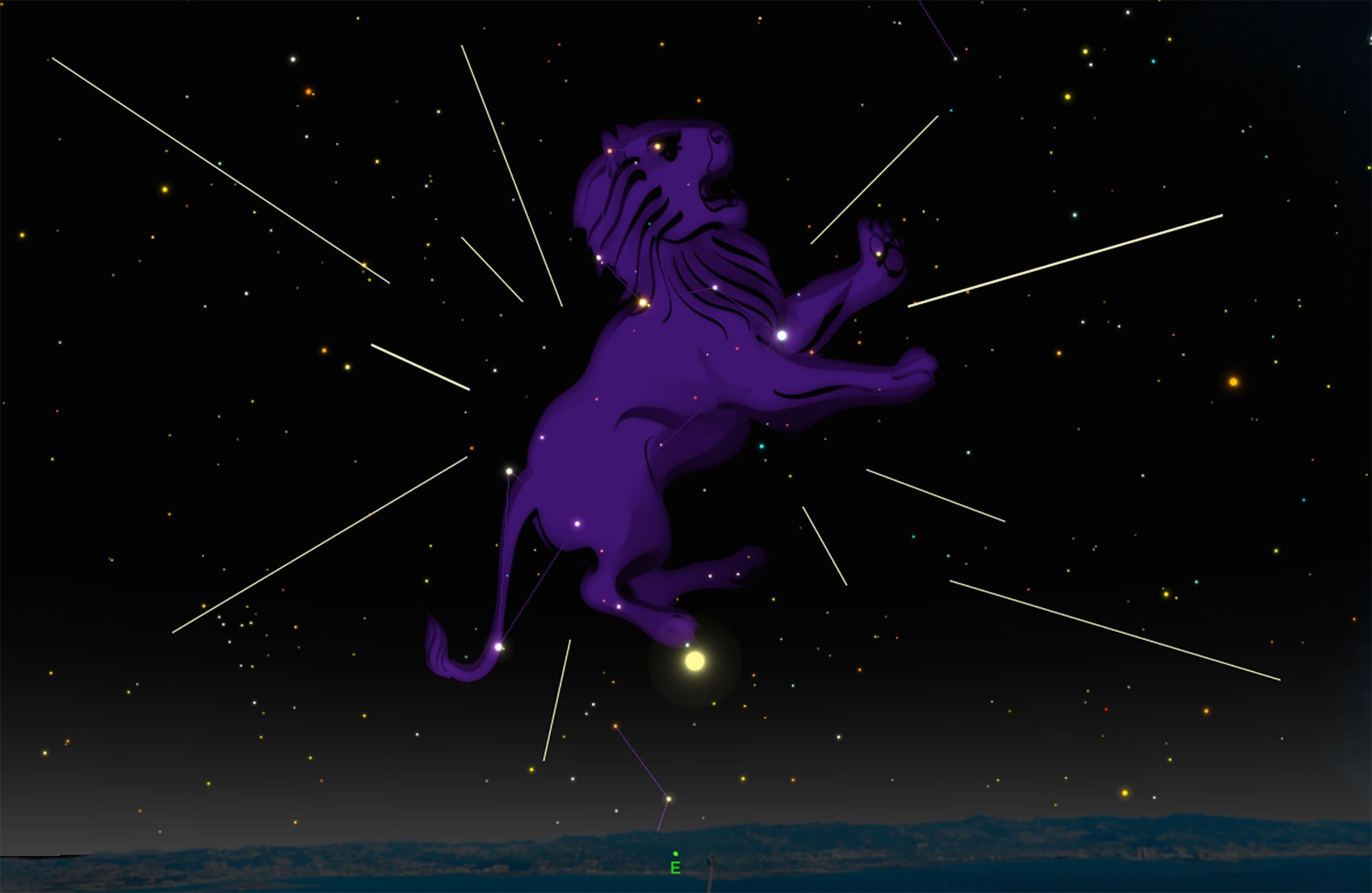

Like most meteor showers, the Leonids are caused by Earth plowing through the dust trail left by a comet. The Leonids come from the trail of the 1.2-mile- (2-kilometer-) wide comet Tempel-Tuttle, which circles the sun every 33 years. When the comet gets close to the sun, melting ice releases pieces of dust—most no larger than a grain of sand—and deposits them in clouds that Earth encounters every year around mid-November.
Even the fainter meteors may be seen after the waxing crescent moon sets and leaves behind dark skies, which will occur by 10 p.m. local time. Lucky North Americans may get an especially good show as the the shower’s peak will occur during the dark overnight period into the early morning hours of Wednesday, November 18.
Saturn Nebula. After nightfall on Tuesday, November 17, and Wednesday, November 18, look for the crescent moon to pair up with a faint, deep-sky treasure dubbed the Saturn Nebula.
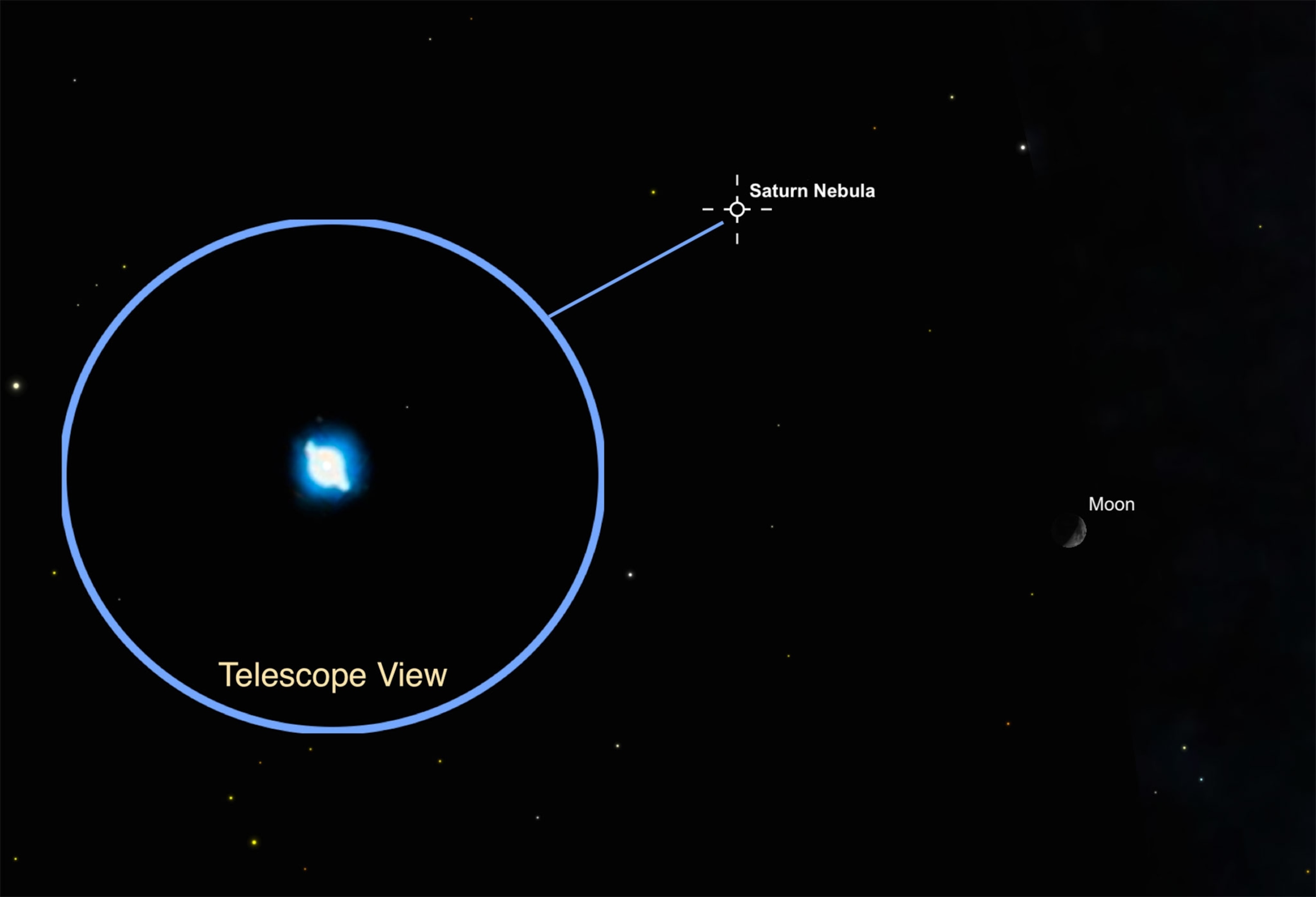
On both nights the two celestial objects will appear separated by only 7 degrees in the sky, slightly more than the width of your first held at arm’s length. At magnitude 7.8, the Saturn Nebula can be glimpsed with a a small backyard telescope and is best seen under high magnification.
The Saturn Nebula isn’t located anywhere near Saturn; this deep-sky object got its name from 18th-century astronomers who thought it resembled the planet Saturn, with rings nearly edge-on. Though the Saturn Nebula may look a bit like a planet, this is actually a planetary nebula, the gaseous remains of a sun-like star, located some 3,900 light-years from Earth and measuring about a half a light-year across. What we see is a shell of glowing gas that was formed when the central star ejected perhaps as much as ten percent of its mass over a period of millions of years.
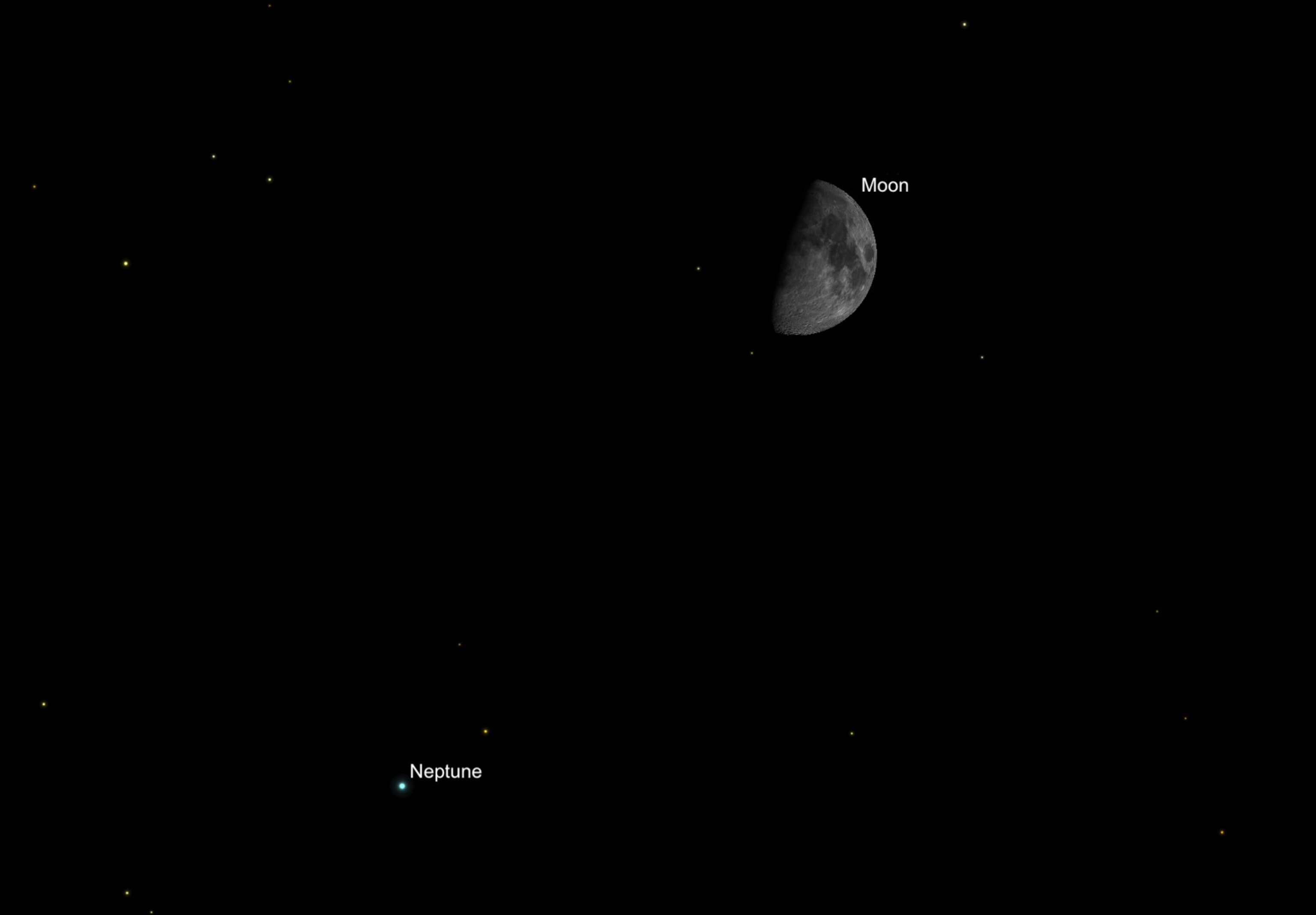
The Moon and Neptune. In the early evening of Thursday, November 19, the near quarter moon will be only 2 degrees from the blue ice giant Neptune.
Spotting the 8th-magnitude planet may be challenging, though, even with a telescope. Neptune will be only four moon disks away from Earth’s lone natural satellite, making the moon a convenient guide but also placing it so close that the lunar glare may drown out Neptune’s faint glow.

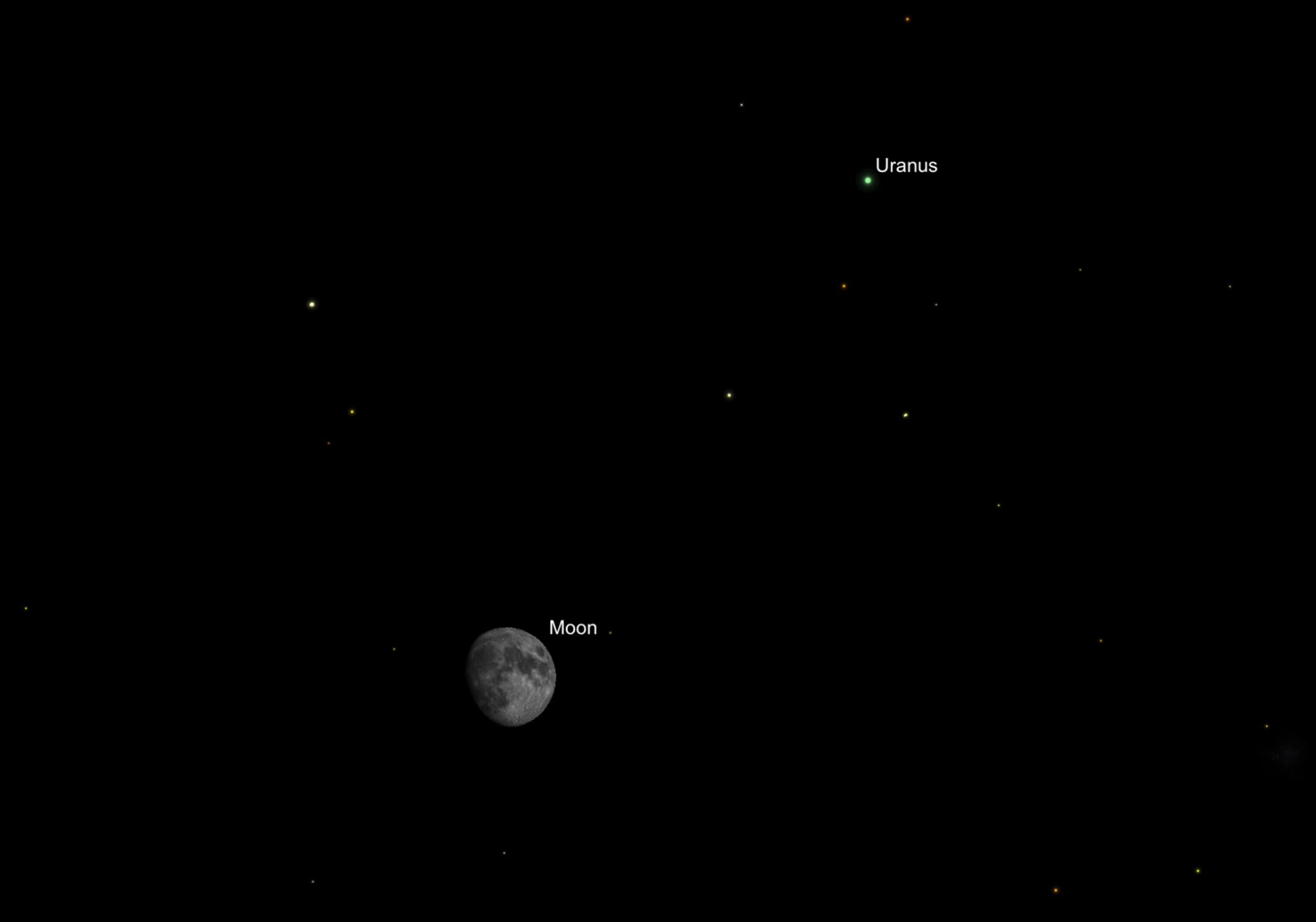
Glimpse of a Green Giant. By the evening of Sunday, November 22, the waxing gibbous moon will pair up with planet Uranus.
The green giant, Uranus, perched 3 degrees to the upper right of the moon, will be an easy target for binoculars even from suburban backyards. Look for the faint 5th-magnitude glow from a tiny green disk in the same field of view as the moon.
