
This Week’s Night Sky: Watch Mars Reverse Its Tracks
The red planet will be in retrograde starting on Saturday, a cosmic illusion that lasts for a few months every two years.
Lunar Seas. As darkness falls on Wednesday, April 13, look for the moon hanging high in the southwestern sky as it reaches its first quarter phase, with half of its disk visible to us on Earth.

With nothing more than your unaided eyes, you should be able to see six dark patches on the lunar surface. These are known as mare, or seas, but they are actually ancient lava plains. When giant asteroids impacted the moon billions of years ago, lava welled up through the resulting cracks and oozed out over the surface, creating the collection of smooth plains.
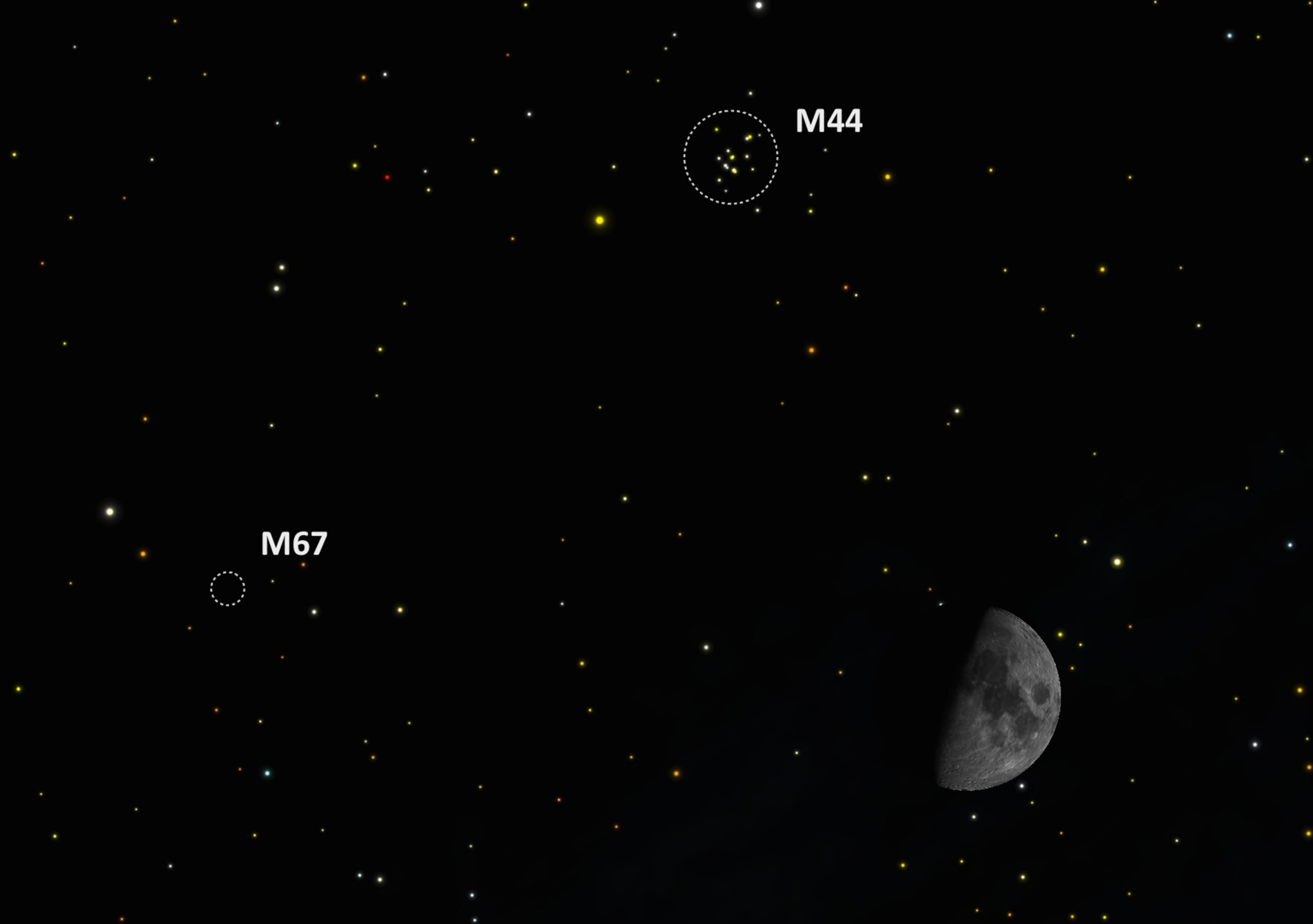
Moon Buzzes Beehive. By Thursday, April 14, the moon will be parked near two beautiful star clusters, both easily visible through binoculars. To the left of the moon will be Messier 67 (M67), an open cluster of about 500 stars that sits 3,000 light-years from Earth.
At the same time, the open cluster Messier 44 (M44), which sits 610 light-years away, will be to the upper left of the moon, forming a neat triangle with M67. Known as the Beehive, M44 is close enough and bright enough to be just visible to the naked eye as a fuzzy spot in the dark sky. Binoculars and small telescopes will reveal about six dozen member stars stretching across 11 light-years of space.
Both clusters will be competing with the glare of the moon, but by the next night they will shine much brighter as the moon sinks closer to the horizon.
Mars Rewind. On Saturday, April 16, the red planet will begin its retrograde motion westward in the sky.
For a couple of months every two years, Mars changes the direction of its motion against the backdrop of fixed stars. This apparent reversal is due to the fact that Earth is orbiting closer to the sun than Mars and is moving faster on its orbital track. That means our planet periodically passes Mars, creating the illusion that it has changed course. Seen from Mars, Earth appears to be in retrograde during this time.

You can track our neighboring ruddy world in the southwestern sky on any clear morning before local dawn. The planet will be in a triangular formation for the next month with the similarly red-colored star Antares below and yellow-tinted Saturn to its left.
Lion’s Heart. Also on April 16, the waxing moon will glide past Regulus, the brightest star in the constellation Leo, the lion. The two objects will appear to be separated by less than three degrees, slightly more than the width of two fingers held at arm’s length.
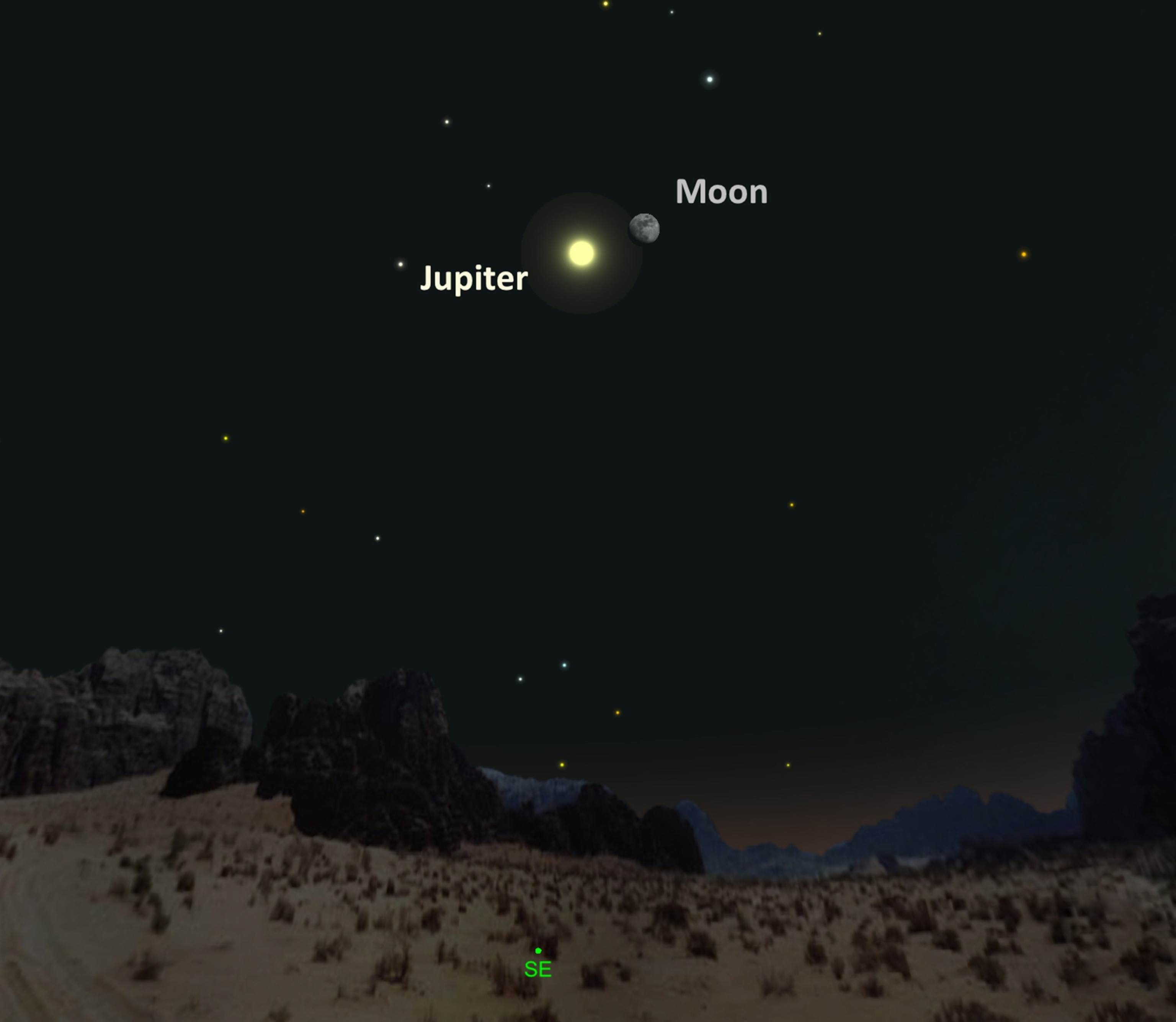
Moon and Jupiter. Finally, if you have clear skies on Sunday, April 17, watch as the moon pays a visit to the brightest planet of the night, Jupiter, as both rise together in the southeastern sky. The two objects will appear to be five degrees apart, roughly equal to the width of three fingers held at arm’s length.
Clear skies!
Follow Andrew Fazekas, the Night Sky Guy, on Twitter, Facebook, and his website.