
This Week’s Night Sky: See Mars and Jupiter Compete
The red planet and giant Jupiter will present prime viewing, while the bright star Arcturus hangs high in the north.
Mars in Charge. While we just passed opposition, when Mars was at its brightest for the year, the red planet will remain at peak visibility for the next couple of weeks. And on May 30, Mars will be at its closest point to us since 2005. The planet will come within 47.2 million miles (75.9 million kilometers) of Earth, making it appear especially big in backyard telescopes.
During this time, look for Mars rising in the east soon after local sunset and travelling across the southern sky during most of the overnight hours, setting in the west before sunrise. By around 1 a.m. local time, the planet will reach its highest point in the southern sky, positioned within the constellation Scorpius.
Mars will appear to have a weaker twin nearby, the orange-hued star Antares. Located 600 light-years from Earth, this red supergiant is 700 times wider than our sun and may explode as a supernova anytime within the next few million years.
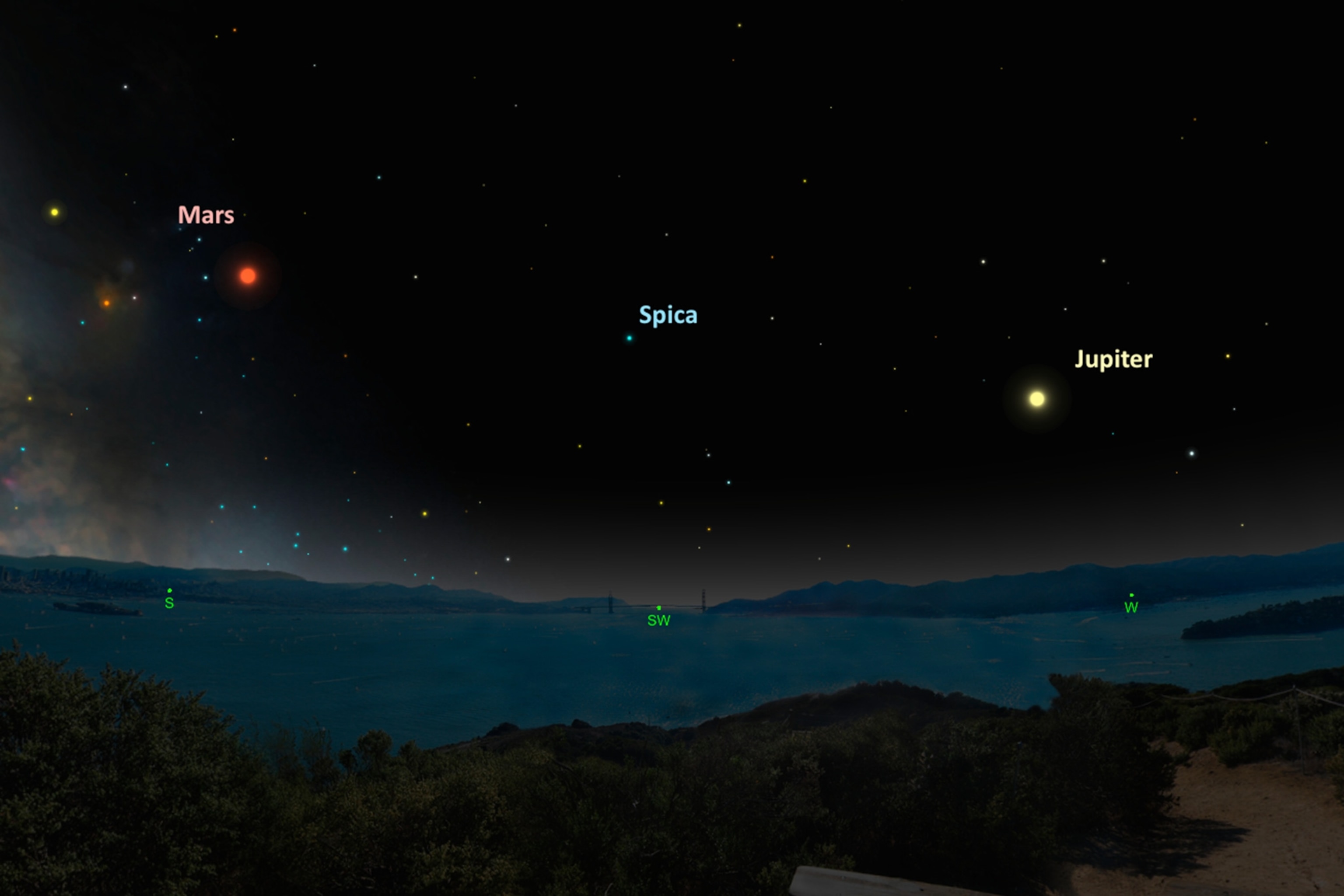
Rival Jupiter. While Mars may be getting all the buzz, the king of all planets will be vying for attention this week, shining high in the southwest skies in the early evening of May 24. Look for Jupiter pinned against the backdrop of bright stars in the constellation Leo, the lion. This stellar pattern is easy to trace out in the heavens, because it actually looks like a giant feline.
For observers in temperate northern latitudes, the planet will set by 2 a.m. local time in the west. Don’t forget to train your binoculars on Jupiter and check out its four largest moons—Io, Europa, Callisto, and Ganymede—which will be lined up on either side of the planet’s equatorial region.
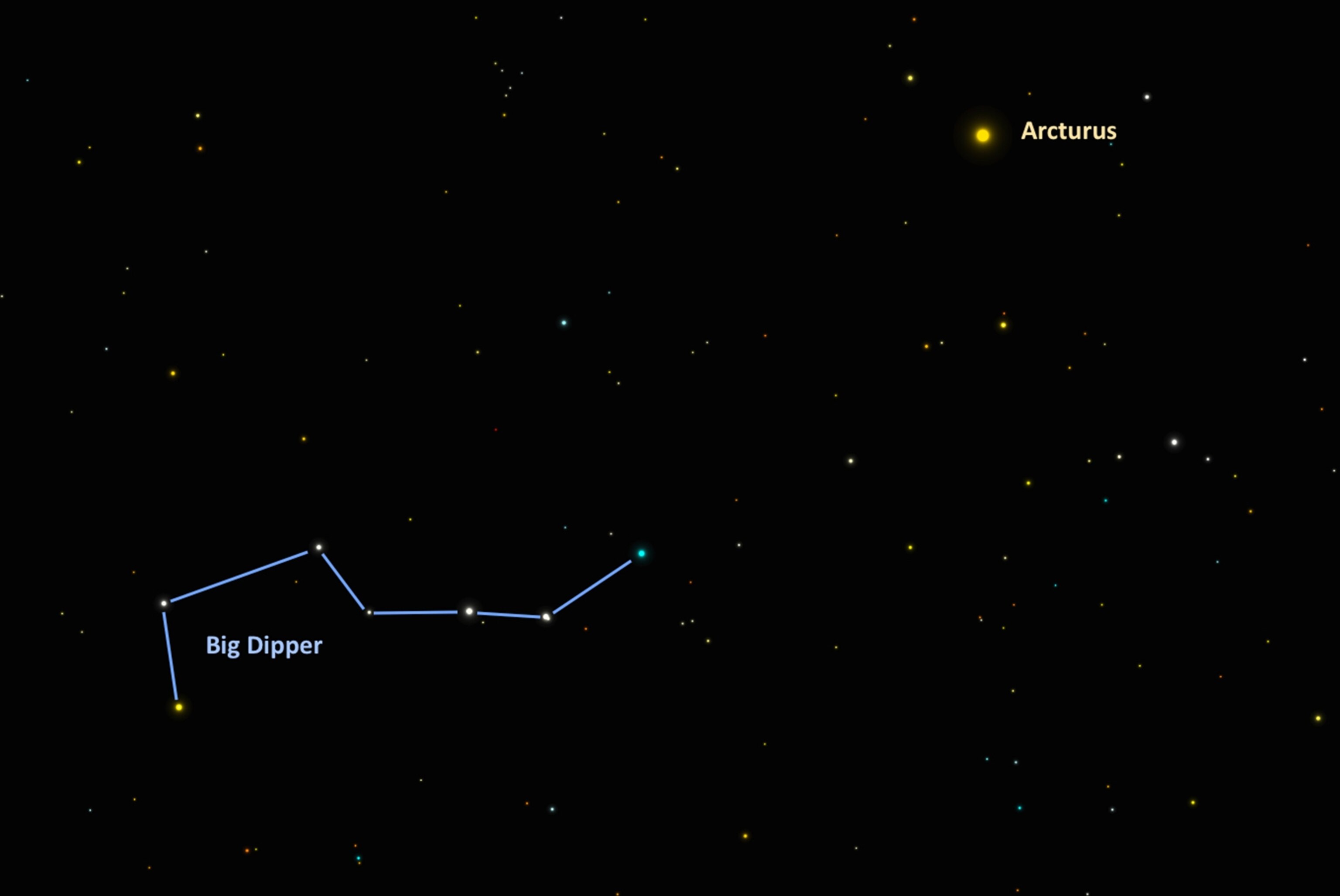
Arc to Arcturus. On May 27, look high in the north after nightfall to see the upside-down Big Dipper. Draw an imaginary line through the handle and follow its arc across the sky until you reach the next brightest star, Arcturus.
Orange-hued Arcturus is a red giant and is the lead star in the kite-shaped northern constellation Boötes, the herdsman. Arcturus, the brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere, sits about 37 light-years away. In 1933, the star’s light was focused through telescopes and used to ceremoniously open the Chicago World’s Fair.
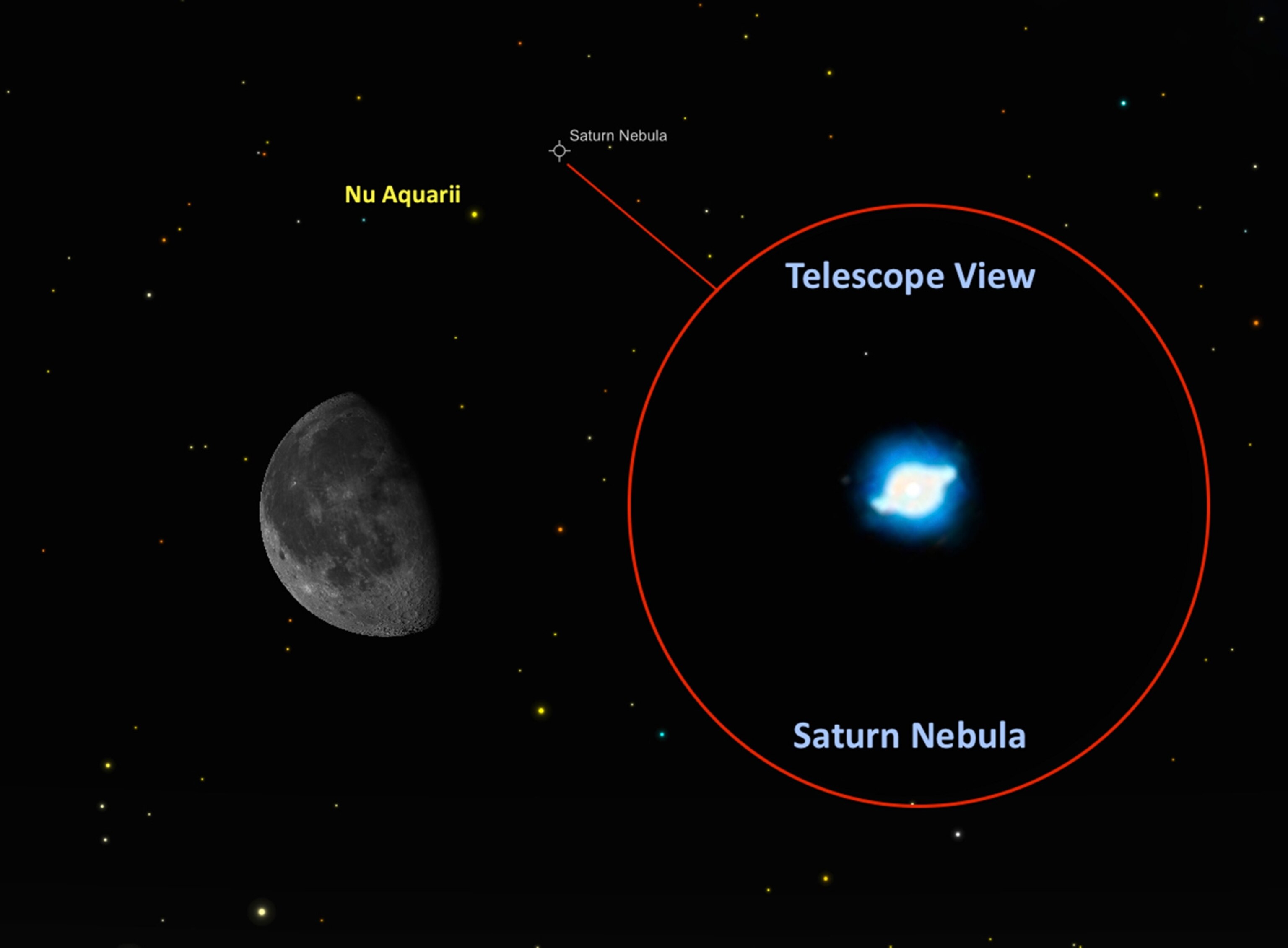
Saturn Nebula. A great observing challenge for backyard telescope owners will present itself in the early morning hours of May 28, when the waning moon will point the way to the secretive Saturn Nebula. This cosmic cloud lies five degrees north of the moon, equal to the width of your three middle fingers held at arm’s length.
At magnitude 7.8, the nebula can be glimpsed with a a small backyard telescope and is best seen under high magnification. You can also look for the very faint naked-eye star Nu Aquarii (4.5 magnitude) sitting only one degree west of the nebula.
This luminescent deep-sky object got its name because 18th-century astronomers thought it had a faint resemblance to the planet Saturn, with rings nearly edge-on. However, the object is actually the gaseous remains of a dead sun-like star.
Lying some 3,900 light-years from Earth, the nebula measures about a half a light-year across. What we see is a shell of glowing gas that formed when the central star ejected perhaps as much as 10 percent of its mass over a period of millions of years.
Clear skies!
Andrew Fazekas, the Night Sky Guy, is the author of Star Trek: The Official Guide to Our Universe. Follow him on Twitter, Facebook, and his website.