You are not venomous. Your spit, while unpleasant, cannot kill. Your dog is not venomous, either. Neither is the squirrel on the sidewalk, the bullfrog in the pond, or the dragonfly floating by your window.
Venom is the mark of a special club, a select subset of the animal kingdom. It includes vipers, jellyfish, spiders, scorpions, centipedes, bees, cone snails, newts, platypus, and even a primate. All these animals produce molecules that attack a victim in minutes or even seconds. The molecules are intricately complex, with shapes that allow them to precisely lock onto certain proteins on our own cells. Depending on its exact target in the body, venom will paralyze nerves, rot muscles, and stop blood from clotting.
Venomous animals are not all closely related to each other. The platypus is much more closely related to us, for example, than it is to a centipede. And that means that venom has independently evolved many times over in the history of life. First there were animals without venom, and then there were.
The origin of new adaptations is one of the most fascinating parts of evolution–from hands to feathers to eyes. But scientists have made exceptional progress in figuring out the origins of venom. Their success may have something to do with the fact that each type of venom is encoded by a single gene. That means that scientists can compare venoms gene by gene to see how they’re related to each other. That’s not to say that the venomous life is a simple one. After all, a rattlesnake produces not one venom but a cocktail of them; the cocktail in another snake will be profoundly different. Delivering the venom also requires a lot of equipment. Venom is produced in special glands, for example, and then has to get transported to the place where it will make contact with its victim–to the skin of a newt, to the tail of a scorpion, to the fang of a cobra. Nevertheless, the molecular elegance of venom lowers a ladder down to scientists, so that they can start their climb into the mysteries of venom evolution.
Recently, some of the world’s experts on venom came together to take stock of what they’ve learned. [pdf] The ways in which venoms emerge, and then evolve, offer lessons for the ways in which any complex new thing comes into being.
Venoms did not pop out of the void. They started out as genes for other functions. Venom genes are closely related to other genes that carry out entirely different jobs, both in venomous animals and non-venomous ones. Some venoms are closely related to immune system proteins, for example, which attack bacteria invading the body. Others are closely related to digestive enzymes
How does an enzyme end up as a venom? There are a number of ways. A common type of mutation causes DNA to get duplicated. At first, the duplication just means that twice as much of the original protein gets made. But then the extra gene can mutate again without harming the function of the original one. A mutation can, for example, change the signal a gene gets about where it should make its protein. Instead of becoming active in the pancreas, for example, it might start making proteins in the mouth.
When an animal bites its prey, the enzyme can then get into the wound. It might happen to have a harmful effect. Even a small effect could help the animal catch more prey, and thus be favored by natural selection. And the new proto-venom gene may undergo more evolution. It may become more and more toxic. Or it may duplicate, and the two venom genes may become deadly in different ways. Two genes can become four, four eight and on and on. The rate at which cone snails duplicate venom genes, scientists have found, is the fastest gene duplication ever found in the animal kingdom.
Each new copy of a venom gene can get fine tuned even further. They may mutate a single base of their DNA, or they may undergo more dramatic changes. Genes are made up of segments called exons, and cells assemble the information in the exons in order to make a corresponding protein. In venom genes, exons sometimes get skipped or shuffled, producing new venom molecules with new properties. These new venoms allow animals to hunt new kinds of prey, or help them do a better job of killing old victims that evolve new defenses.
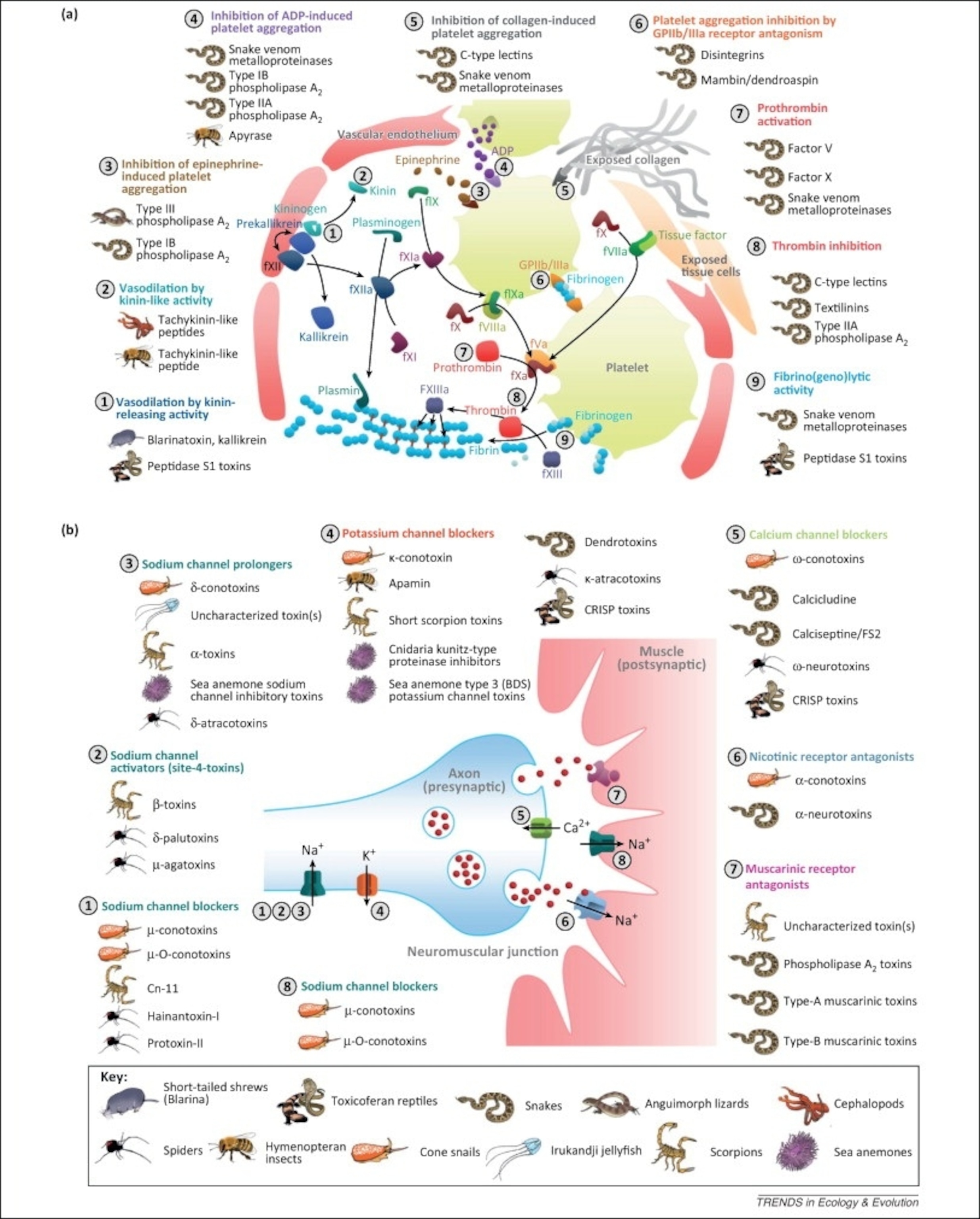
Each lineage of venomous animals became deadly on its own, independent of all the others. And yet, in the end, their venoms echo each other. I’ve reprinted a crazily detailed figure below, which you can enlarge by clicking on the image. It shows how different animals have ended up with venoms that zero in on the same molecular targets. The targets fall into two main categories: the channels and receptors on neurons, and the molecules involved in clotting blood. For example, cone snails, scorpions, and anemones have all evolved venoms that attack channels on neurons that pump out potassium. Snakes and bees have evolved the ability to block platelets from clumping together, a crucial step in blood clotting. These results show that there are a limited number of ways to kill your victim quickly. No matter what genes you borrow for the evolution of venom, they will end up very similar to other venoms.
There’s a lot left for scientists to discover about venom evolution. One of the most surprising recent discoveries is that the borrowing involved in venom evolution doesn’t go one way. Take the natriuretic venom found in snakes like the pit viper. It evolved from proteins found in other animals (including us) which relax the walls of blood vessels. In snakes, it evolved into a venom that relaxes blood walls so fast that it causes a debilitatingly rapid drop in blood pressure. But in pit vipers, one of these natriuretic venoms is produced inside their brain.
No one knows what this venom is doing inside the snake’s brain. But it’s obvious what it’s not doing: killing prey. It’s likely that the venom, borrowed from other parts of the body, has now been borrowed back. That’s one of the most interesting evolutionary lessons that venom has to offer: it’s endlessly creative, yet remarkably frugal.