Reports are coming out this morning on a new study on one of the Loom’s favorite organisms: Toxoplasma gondii, the single-celled parasite that lives in roughly half of all people on Earth and has the ability to alter the behavior of its host. I reported on the research last June in the New York Times, when the Stanford researchers reported their results at a scientific conference. It’s nice to finally get the results on paper, though.
The study is a fine example of an underappreciated part of science: replication. In 2000 British researchers carried out a study in which they put healthy and Toxoplasma infected rats in an outdoor enclosure and watched them nose around. They added odors to some of the corners of the enclosure; sometimes the odor of rats, sometimes of rabbits, sometimes of cat urine. They found that healthy rats were deeply affected by the scent of a cat, becoming less curious. Parasite-infested rats showed no fear. They proposed that the shift in behavior was an adaptation of the parasite for getting into its final host–cats. (I included a description of this study in my book Parasite Rex.)
It was a remarkable result, but even remarkable results may not be so significant as they seem at first. They need to be replicated by other researchers. That’s what the Stanford team has now done. They set up an enclosure, set both rats and mice loose in it, and observed a significant difference between infected and parasite-free hosts. The animals were actually attracted to the smell of cats. The Stanford team went beyond mere replication, however. They took a closer look at how the parasites manipulate their hosts.
(Toxoplasma – the brain parasite that influences human culture)
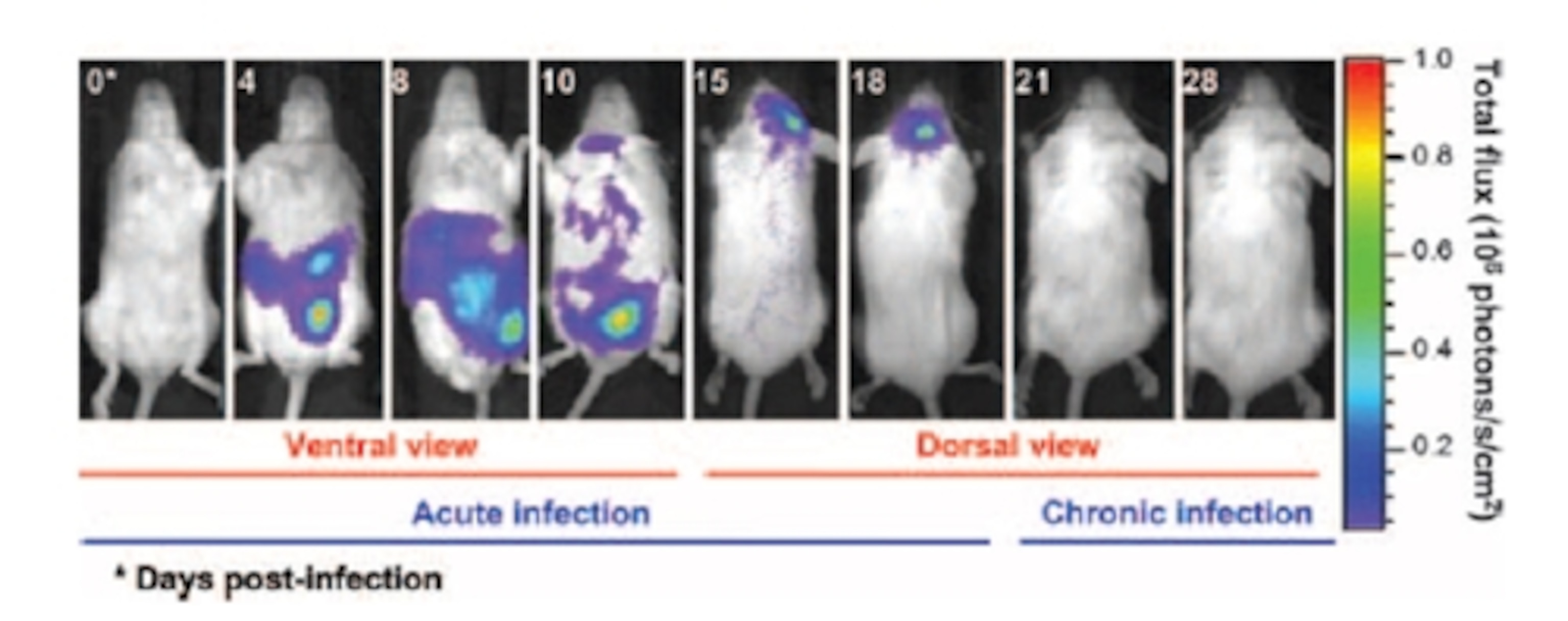
For example, they found that even though the hosts lost their fear of cats, they still had normal anxiety in other respects, and could learn to become frightened of things. This is intriguing, since innate fears (such as the fear of cat urine) is the product of many of the same neurological circuits that produce learned fear and anxiety. Toxoplasma is particularly fond of living in the brain, where it forms cysts. The researchers mapped the parasites in the brain by adding a light-producing gene to them. As the parasites moved through their hosts, the light leaked out, and the scientists could photograph their journey (see the illustration above). They found that an unusual number of Toxoplasma ended up around the amygdala, a structure in the brain that’s important for fear responses. (When the paper goes online this week, it will be here.)
While this is all extremely cool, scientists still have a lot to learn about Toxoplasma. Some recent research on the history of Toxoplasma doesn’t fit comfortably with an image of the parasite as always trying to get its hosts into the jaws of cats. It’s only in cats that Toxoplasma can reproduce sexually. Two parasites mate and their offspring–egg-like cells called oocysts–carry a mix of their genes. But Toxoplasma can also reproduce like a clone, splitting in two, either in cats or outside them. The variation in genes from one Toxoplasma to another records the history of the parasite’s reproduction. Cloning creates lots of parasites that are almost identical, genetically, while sex mixes them up in distinctive ways.
It turns out that most Toxoplasma in North America and Europe belong to three lineages that share a common set of parental strains that lived 10,000 years ago (nicknamed Adam and Eve). Once those three lineages emerged, they exploded. But they show little sign of sex. For the most part they just cloned themselves. It’s not clear whether getting into a cat was all that important to the reproductive success of these dominant strains. (The other strains of Toxoplasma elsewhere in the world have yet to be studied closely.) It’s possible that Toxoplasma’s host manipulation is an ancient adaptation that’s become a bit obsolete in modern strains, or perhaps it evolved thanks to the slight reproductive edge it gives over the course of many generations. (Sexual reproduction from time to time may be essential for the survival of a lineage.)
Despite these uncertainties, the new study certainly adds more weight to the notion that Toxoplasma has unconsciously figured out some key features of the mammal brain–features of fear and drug delivery that we don’t yet understand. Just like wasps that perform brain surgery, these are parasites worth learning from.