
Two potentially life-friendly planets found orbiting a nearby star
“We will eventually see if they are actually habitable and, perhaps, even inhabited,” astronomers predict.
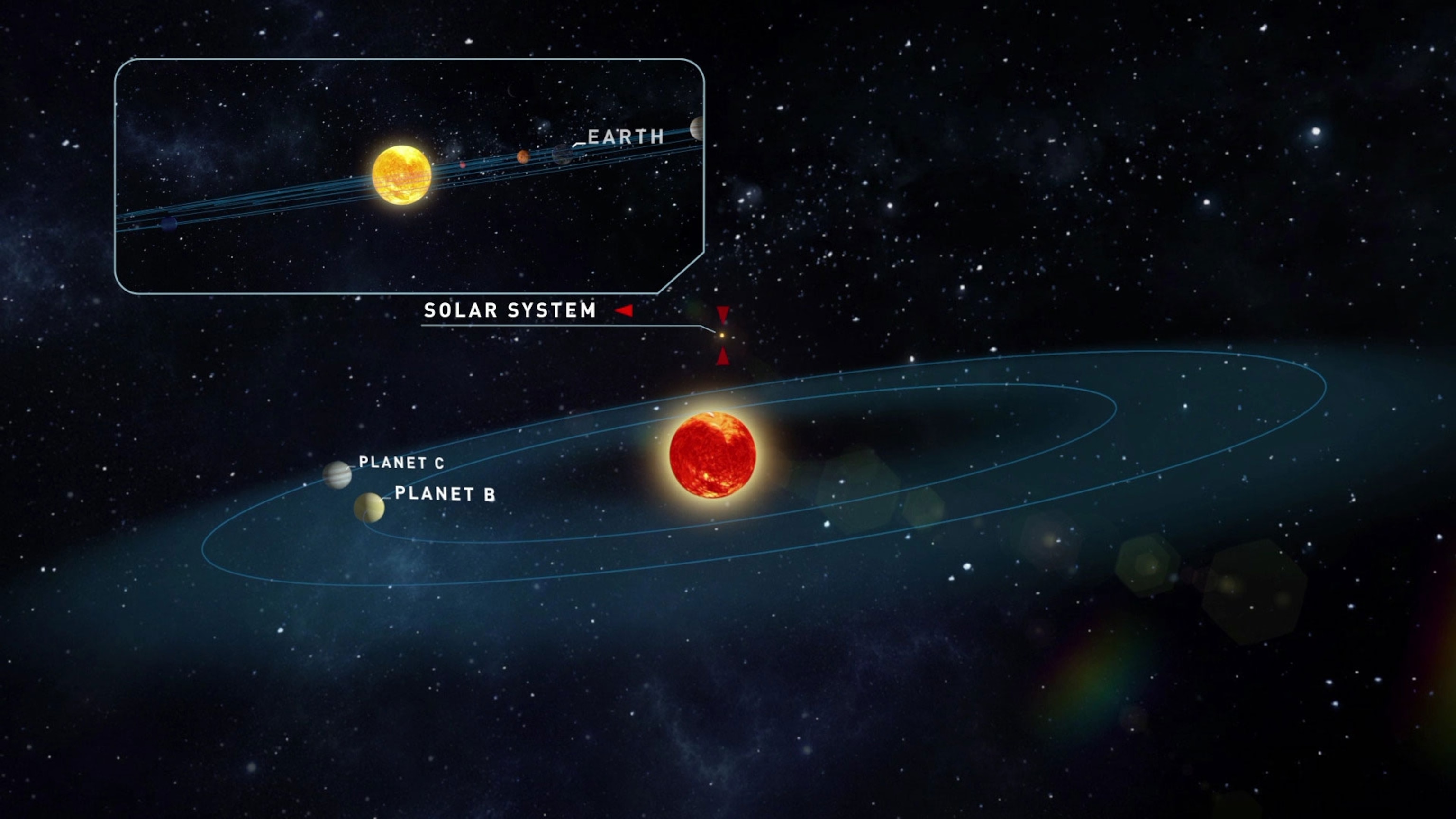
A tiny, old star just 12 light-years away might host two temperate, rocky planets, astronomers announced today. If they’re confirmed, both of the newly spotted worlds are nearly identical to Earth in mass, and both planets are in orbits that could allow liquid water to trickle and puddle on their surfaces.
Scientists estimate that the stellar host, known as Teegarden’s star, is at least eight billion years old, or nearly twice the sun’s age. That means any planets orbiting it are presumably as ancient, so life as we know it has had more than enough time to evolve. And for now, the star is remarkably quiet, with few indications of the tumultuous stellar quakes and flares that tend to erupt from such objects.
These factors, plus the system’s relative proximity, makes the system an intriguing target for astronomers seeking to train next-generation telescopes on other worlds and scan for signs of life beyond Earth.
“Both Teegarden’s planets are potentially habitable,” says Ignasi Ribas of the Institute of Space Studies of Catalonia, a member of the team reporting the planets today in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics. “We will eventually see if they are actually habitable and, perhaps, even inhabited.”
Stellar runt
The two worlds orbit a star so faint that it wasn’t even spotted until 2003, when NASA astrophysicist Bonnard Teegarden was mining astronomical data sets and looking for dim, nearby dwarf stars that had so far evaded detection.
Teegarden’s star is a stellar runt that’s barely 9 percent of the sun’s mass. It’s known as an ultra-cool M dwarf, and it emits most of its light in the infrared—just like the star TRAPPIST-1, which hosts seven known rocky planets. But Teegarden’s star is just a third as far from Earth as the TRAPPIST-1 system, which makes it ideal for further characterization.
Ribas and his colleagues are currently searching for planets orbiting 342 small stars, so they aimed the CARMENES instrument, located at Spain’s Calar Alto Observatory, at the mini-star.
CARMENES observed Teegarden’s star over three years, watching for the wiggles and tugs produced by any orbiting planets. In the end, more than 200 measurements suggested that two small worlds are jostling the star, each weighing in at approximately 1.1 times Earth’s mass. The team calculates that one of the planets, called Teegarden’s star b, completed an orbit in a mere 4.9 Earth-days; the other world, Teegarden’s star c, has an orbit of just 11.4 days.
Eerily quiet
Before they could report that those planets likely exist, the team had to rule out intrinsic stellar phenomena, like star spots and flares, that can masquerade as orbiting worlds. Sometimes, this can be quite tricky for red dwarf stars, which are notoriously tempestuous and prone to erupting in massive flares. But Teegarden’s star is almost eerily quiet, making it much easier than usual to tease out planetary signals.
“The number of measurements is so high and the star is so well-behaved that there is very little room for an alternative explanation,” Ribas says. “So, this is, to me, a clear-cut case of planet detection. I would bet both my little fingers that they are there.”
“These are very plausible-looking planet candidates,” agrees Lauren Weiss, of the University of Hawaii. “I am impressed by the quality of the data.”
However, Weiss notes, a few points cause her to hesitate. First, scientists don’t know the exact time it takes for Teegarden’s star to rotate on its axis, and that type of motion could be masquerading as one of the planet signals.
Still, “stellar rotation would probably only mimic the orbit of one planet, not two planets, so at least one of the planets is probably real,” she says.
Second, she says, it’s possible the planets might be zipping around the star more speedily than inferred, which might knock down their potential habitability.
“This technical concern is minor though,” Weiss says. “If there really are planets around the star, and the authors got their orbital periods wrong, the planets are still planets.”