
This Week’s Night Sky: See Shooting Stars and a Cosmic Crab
Also this week, the moon briefly blots out a star and Jupiter sinks into the west.
Jupiter Sinking. After sunset on July 25, start looking for superbright Jupiter hanging low in the western sky.
The gas giant sits below the back foot of the constellation Leo, the lion, which is a springtime star pattern that is now setting quickly in the west. That means now is the time to catch sight of the largest planet in the solar system before it gets too close to the sun and gets lost in its glare in about a month’s time. For observers in the Northern Hemisphere, Jupiter currently appears about 20 degrees above the horizon just after local sunset, about equal to the width of two of your clenched fists stacked on top of each other.
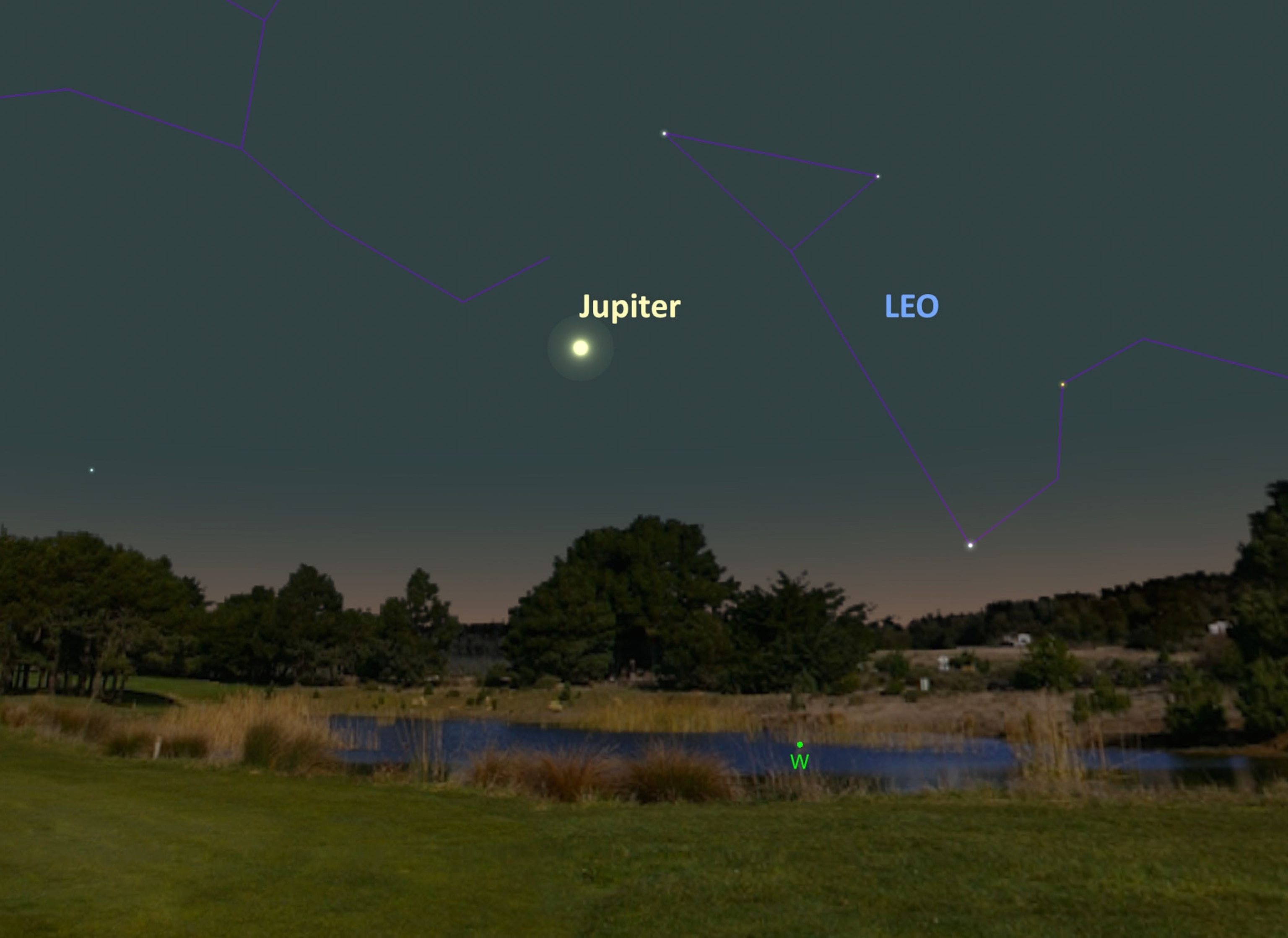
While Jupiter alone appears dazzling to the unaided eye, binoculars will reveal four of its largest moons lined up beside the planet. And small telescopes will yield even more stunning views, showing the planet’s disk covered with cloud bands and other distinctive atmospheric features, including a giant oval storm called the Great Red Spot. (See Jupiter through the eyes of NASA’s Juno spacecraft, which is now orbiting the giant planet.)
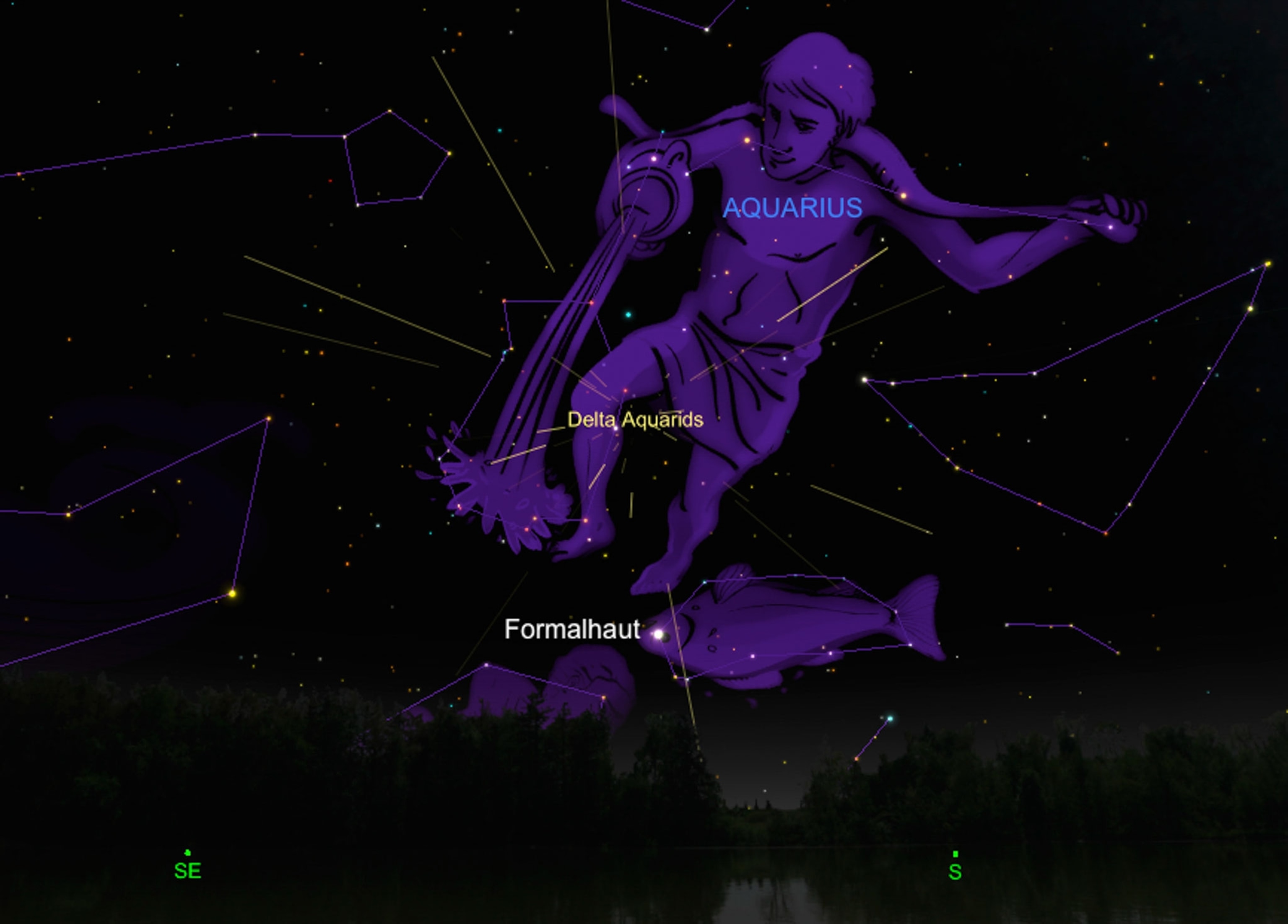
Delta Aquarids. As we wait for the Perseids, the granddaddy of all shooting star shows, in August, a modest but dependable meteor shower called the Delta Aquarids will whet our appetites this week.
Officially peaking in the early morning hours of July 28, the Delta Aquarids should be at their best for a couple days on either side of the peak. The individual shooting stars will appear to radiate from the shower’s namesake constellation, Aquarius, the water bearer, which rides the low southern horizon.
From the dark countryside away from city lights, this shower can produce upward of 20 meteors an hour between midnight and dawn. However, with the waning crescent moon rising at around 2 a.m. local time, the extra light in the sky will make meteors harder to see, and the numbers may be a bit lower than usual.
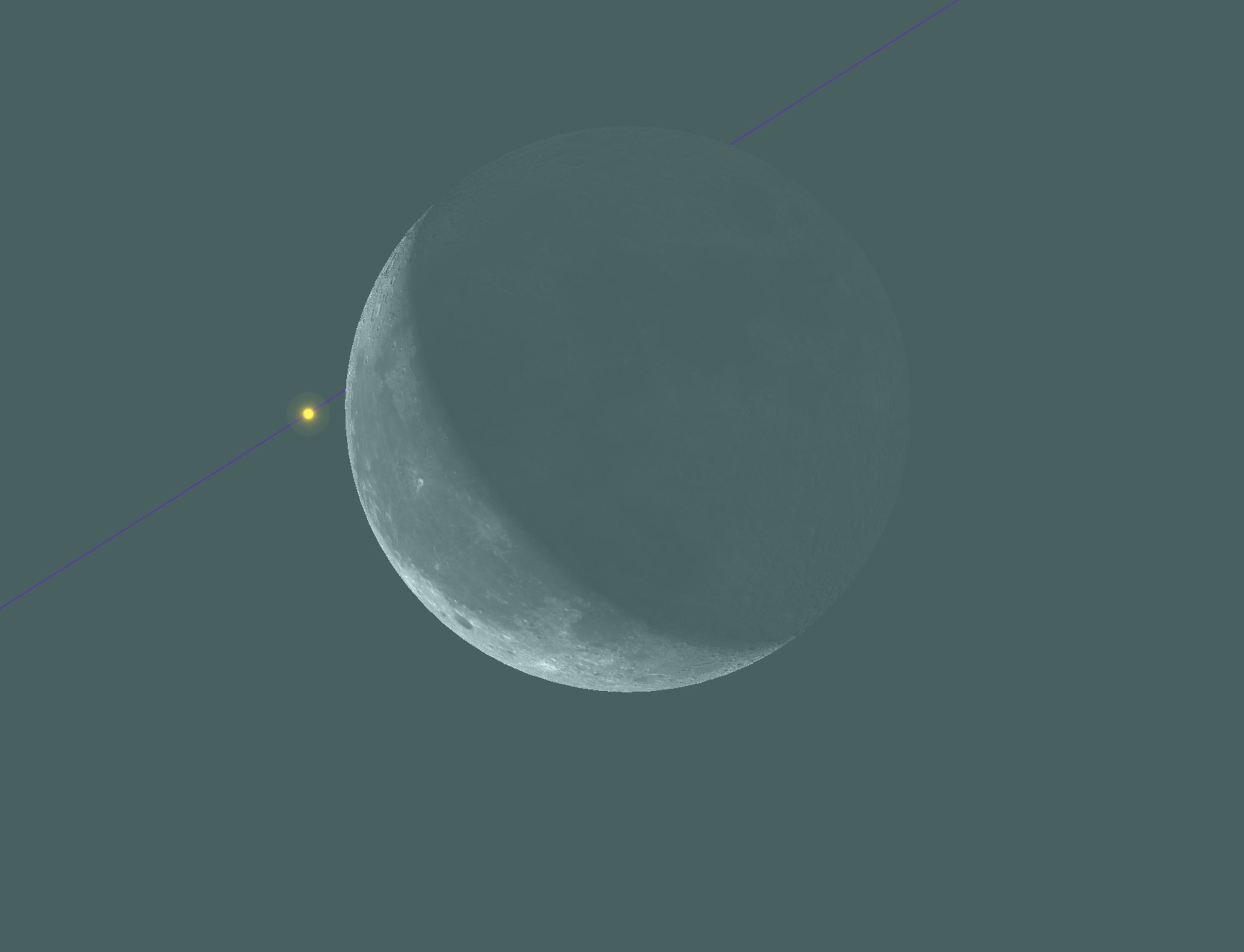

Bull’s-Eye Winks. In the early morning of July 29, lucky sky-watchers across eastern North America will get to witness the waning crescent moon briefly cover up a bright orange star.
The 65-light-year-distant red giant Aldebaran will be eclipsed by the moon for observers from southern New Mexico to northern Maine, according to Astronomy.com. Observers in locations north of this line will see Aldebaran instead make a very close pass above the moon. The event will be best seen through binoculars and telescopes due to the bright glare of the moon but should still make for a great observation challenge for unaided eyes.
Check out event details and times for specific locations here.
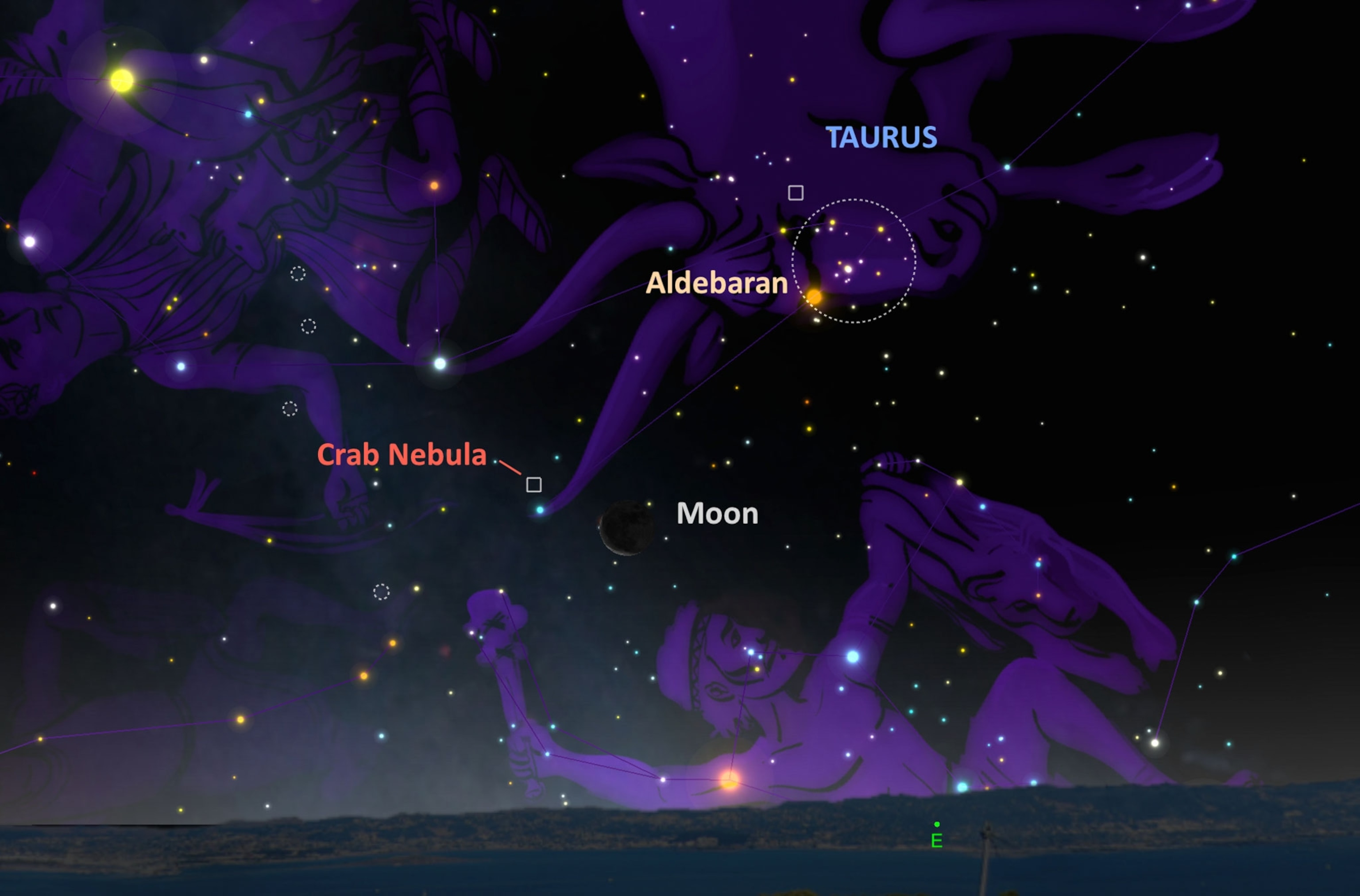
Crab Nebula. In the early morning hours of July 31, backyard telescope users can hunt down the most famous and arguably best example of a supernova remnant, thanks to the moon pointing the way.
Look for the faint object known as Messier 1 or the Crab Nebula approximately five degrees above the thin crescent moon, or about the width of your fist held at arm’s length. The Crab Nebula shines at magnitude 9 and sits about 6,500 light-years from Earth. That’s close enough that people on Earth saw the supernova in the year 1054 A.D. (See a spectacular Hubble image of the heart of the Crab Nebula.)
Clear skies!
Andrew Fazekas, the Night Sky Guy, is the author of Star Trek: The Official Guide to Our Universe. Follow him on Twitter, Facebook, and his website.