Water Found Deep Inside the Moon—Get the Facts
Satellite data suggest that water inside the moon is widespread, and that volcanic rocks may be a valuable resource for future explorers.
There's even more water on the moon than we previously thought, according to new analysis of tiny glass beads left over from ancient volcanic eruptions.
The naturally occurring beads were collected in the 1970s as part of the Apollo 15 and 17 missions, which landed near zones of volcanic activity. The beads formed when magma bursting onto the surface crystallized in such a way that water became trapped inside.
However, scientists couldn’t be sure if the Apollo samples are unique or if other volcanic flows on the moon are filled with water-bearing glass. (Find out how flying oceans of magma help demystify the moon's creation.)
In a new study published today in Nature Geoscience, scientists reexamined the Apollo samples and used more recent satellite data to look for signs of water-bearing beads elsewhere on the moon. They found that the volcanic deposits are indeed widespread, which suggests that the material inside the moon is wetter than previously thought.
“The fact that they see this feature associated with the glasses tells us that there was indeed quite a bit of water in the interior of the moon when these volcanic eruptions were occurring,” says Anthony Colaprete, a NASA scientist who reviewed the paper.
Here’s what we now know about water on the moon.

Has Anyone Found Water on the Moon Before?
Yes, but only very recently. Scientists used to think the entire moon was bone-dry. But in 2008, researchers examined those glass beads from the Apollo samples and found the first known trace amounts of water.
From that point on, lunar water discoveries started gushing. In 2009, NASA crashed a rocket and a satellite into a crater on the moon’s south pole, in the hopes of picking up additional watery evidence. The crashes gave off signatures associated with water ice and hydroxyl—a highly reactive molecule associated with water.
And in 2010, scientists looked closer at other collected moon rocks and found more signatures of water in a mineral called apatite. That’s when geologists began suspecting that the moon holds hidden reservoirs locked in its rocks. If you were to take all of the water in the moon’s interior, it would create a one-yard-deep ocean covering the entire surface, geologist Francis McCubbin estimated at the time.
How Is This Study Different?
While we’ve mapped a good amount of the moon’s surface water, we don’t know for sure what the interior of the moon is like, in part because we have very few samples of volcanic rocks belched up from the lunar mantle.
For their study, Ralph Milliken of Brown University and Shuai Li at the University of Hawaii wanted to find out more about the amount of water inside the moon. (See rare pictures of the moon captured by Apollo astronauts.) The study is one of the first to try and answer this question using satellite mapping of volcanic debris called pyroclastic flows.
So How Much Water Is There?
Unfortunately, while this study suggests water is indeed more abundant inside the moon, it’s hard to know for sure how much exists.
Studies from 2011 revealed that the volcanic beads contained similar amounts of water as volcanic basalts on Earth. And deep within our planet, there is probably more water than all of the surface oceans, lakes, and rivers combined.
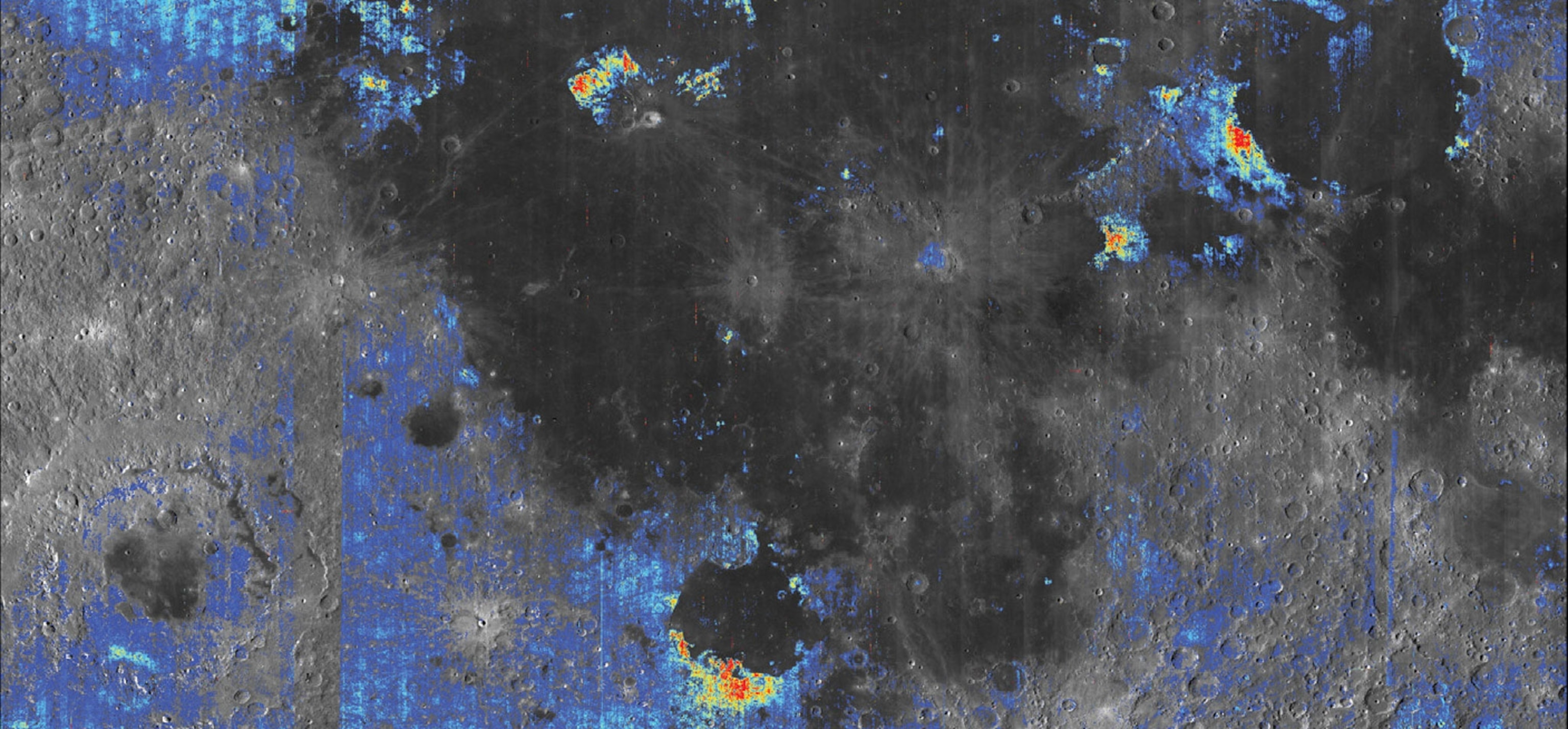
This new finding could mean that at least part of the moon’s mantle might have as much water as Earth’s. (Read more about how Saturn's largest moon could have the components needed for life.)
What Does This Mean for the Future?
Even though the glass beads contain only 0.05 percent water, the sheer amount of them presents a tantalizing opportunity for future moonwalkers. Water ice in deeply shadowed polar craters would be much harder to reach than the water-bearing volcanic rocks spread across the moon. That means lunar visitors could one day extract this water rather than having to bring their own supplies.
“This is actually very useful,” says Colaprete. “We can actually now have a better handle on these deposits as a potential lunar resource going forward and can be compared to future studies of polar resources.”