
Rare Solar Navigation Tool Found in Ancient Shipwreck
The device was found on a ship that once belonged to a fleet led by Vasco da Gama during Europe's 'Golden Age of Exploration."
When a small, 500-year-old copper disk was discovered among the remains of a shipwreck off the coast of Oman in 2014, archaeologists suspected it was a navigation tool called an astrolabe.
Now, thanks to 3D scanning technology, scientists are able to see the small faded measurements etched into the disk—which confirm that it is in fact an astrolabe. It is also now thought to be the earliest such find from a period known as the European Age of Exploration.
The disk was found on a ship called the Esmeralda, which belonged to a fleet led by the famous Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama during his search for a route from Europe to India in 1502-1503.
In 2014, a team of excavators led by marine scientist David L. Mearns and his company Bluewater Discoveries Ltd. loosened the astrolabe from sand covering hundreds of other relics that sat on the sea floor. In an interim report they published last year on the find in the International Journal of Nautical Archaeology, they theorized that the disk was used for navigation.
A Portuguese royal coat of arms was visible on the disk's top half, and on the bottom was an etching of an armillary sphere, which Mearns claimed belonged to Portuguese King Dom Miguel. These etchings indicated to archeologists that the object was a "high-status" object aboard the Esmeralda.
While these markings suggested that the disk was used for navigation, Mearns and his team needed more proof before they could declare it with certainty.
That's where Mark Williams, a professor at the University of Warwick, and a team of engineers came in. They flew to Oman to scan and render 3D images of the 500-year-old artifact. Using a laser scanner that produces 80,000 measurement points per second, they were able to create a 3D model of the astrolabe.
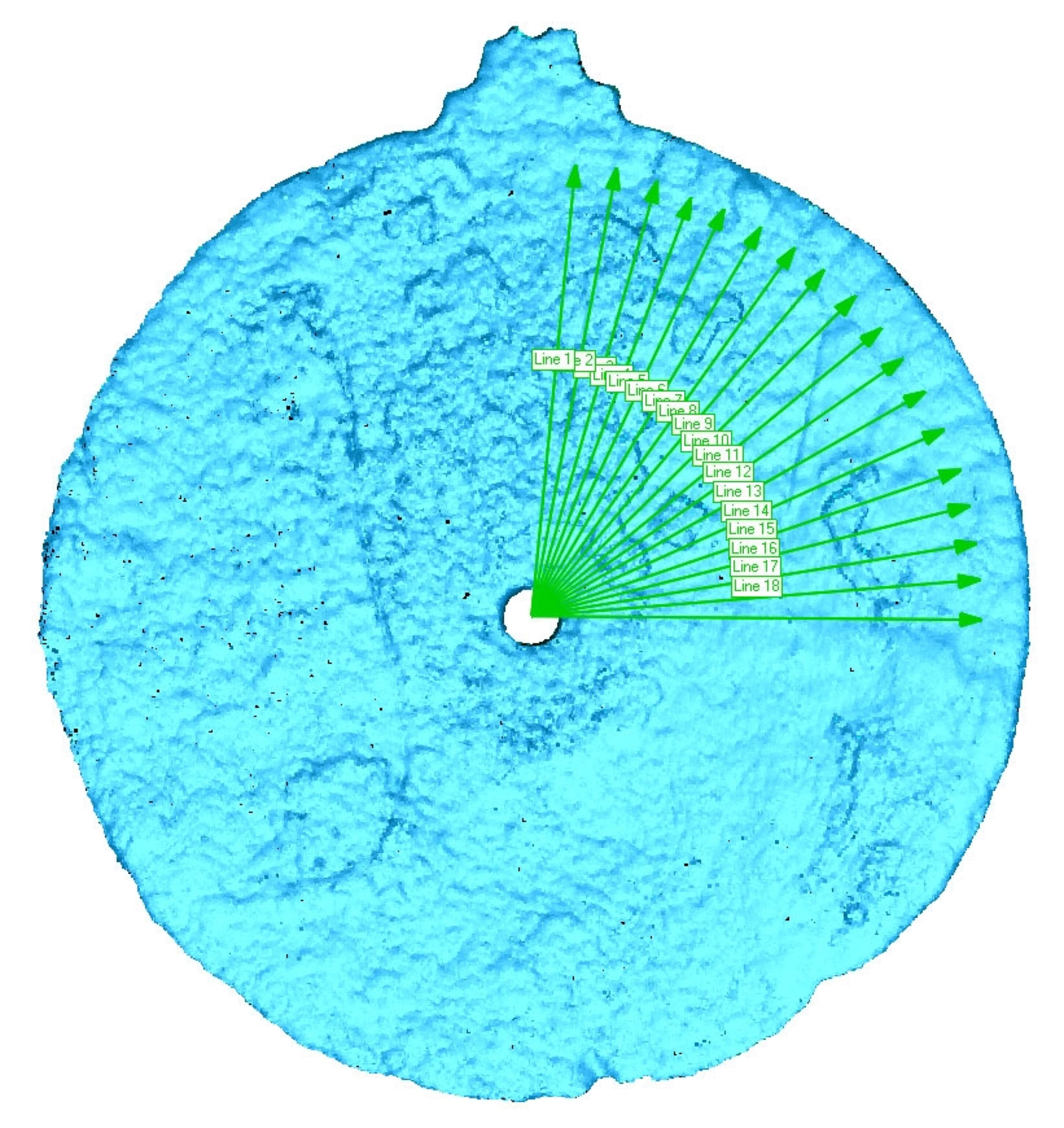
What they saw on the scans wasn't visible to the naked eye—eighteen individual lines emerging from a hole in the center of the disk and arranged at five-degree increments.
"The markings were very fine and, due to damage to the surface, almost invisible to the human eye," said Williams. "The resolution of the 3D data allowed us to zoom in and identify the marks and subsequently characterize them."
Markings on astrolabes are used to measure angles. They're one of human civilization's most advanced ancient tools and are thought to have become popular just prior to the current era. By aligning an astrolabe perpendicular to the horizon, ancient astronomers could calculate measurements like time and position.
Astrolabes used by early sea explorers are frequently referred to as mariner's astrolabes. A broken bracket at the top of the disc indicates it was likely suspended to align it perpendicularly to the horizon. By measuring the altitude of the sun at noon, navigators could then measure the sun's declination, which accurately told sailors their latitude.
An Age of Discovery
The 15th century to the 17th century marked a period of booming European exploration, during which time European nations were fervently searching for maritime routes.
When da Gama embarked on his second voyage to India, around 1502-1503, he took with him a fleet of 20 ships, including the Esmeralda. European interest in Indian spices burgeoned during the 15th century, but passage to India was largely controlled by Arab rulers. da Gama become the first to chart a nautical path directly to India by sailing around the horn of Africa.
Stories passed down from witnesses and damage on part of the ship's remains indicate it probably sank from a storm that smashed it into deadly rocks. The remains were initially located in 1998, but it wasn't until 2013 that Mearns—supported in part by the National Geographic Society Expeditions Council—unearthed thousands of the ship's treasures.
(Read more about the Esmeralda and the explorers who discovered it.)
"We really don't know much about early astrolabes, so this one is precious from that viewpoint," said Luis Filipe Viera de Castro, a professor of nautical archaeology at Texas A&M University. Previously, the earliest known example of a mariner's astrolabe was dated to a 1554 Spanish shipwreck that sank near the coast of south Texas.
"It is also precious because it almost certainly comes from one of Vicente Sodré's lost ships, and these were probably the first European warships to enter the Indian Ocean," said Castro.
Vicente Sodré was da Gama's maternal uncle and commander of the Esmeralda. Cannonballs bearing his initials were found among the watery wreckage. Instructed by da Gama to guard Portuguese factories off the coast of India, the Sodré brothers instead sailed to the Gulf of Aden, where they looted Arab ships. Both Vicente and his brother Brás died when the ships sank during a storm.